Nelson will be honored as the inaugural grant winner at the Gem Awards gala on March 13.
8 Key Changes the FTC Made to the Jewelry Guides
Learn more about the new terms for lab-grown diamonds and composite gemstones, and the major changes in store for precious metals jewelry.

The Jewelry Guides are guidelines the FTC provides on the terms used in marketing and advertising gems and jewelry.
While they are not official laws or regulations, JVC President Tiffany Stevens said those that do not follow the guidelines run the risk of being sued by a competitor, sued by a consumer and/or hit with civil penalties by the FTC.
The publication of the final version of the Jewelry Guides follows six years of back-and-forth between the industry and the commission, and many of the changes included do not vary greatly from the proposed changes the FTC released in 2016.
On Tuesday, National Jeweler spoke with Stevens and JVC Senior Counsel Sara Yood about the most significant changes to the guides, starting with the contentious battle over the terminology used to describe man-made diamonds.
1. The FTC is allowing the use of the word “cultured” in connection with lab-grown diamonds, but not by itself.
The FTC said cultured can be used in connection with lab-grown diamonds as long as it is “immediately accompanied, with equal conspicuousness” by one of the following terms: laboratory-created, laboratory-grown, [manufacturer name]-created, or by some other word or phrase of “like meaning.”
The commission said it received a total of 21 comments on this issue, and none of the commenters agreed with its position.
Lab-grown diamond sellers, like the Diamond Foundry and the International Grown Diamond Association, advocated for the use of the word cultured by itself, while other organizations, including the JVC and the Diamond Producers Association, pushed back against it.
They argued that lab-grown diamonds are not “natural” and using the word cultured would mislead consumers into associating the man-made stones with the organic process used to cultivate pearls.
In the end, the FTC opted to allow “cultured” into the lab-grown diamond lexicon but not without additional qualification.
2. “Synthetic” was removed from the recommended language for lab-grown diamonds, but that doesn’t mean it can’t be used.
Here’s what the FTC’s revised Jewelry Guides state about the use of the term synthetic: “Given the likelihood of consumer confusion, the final Guides do not include ‘synthetic’ among the examples of terms that marketers may non-deceptively use to qualify claims about man-made diamonds, thus eliminating the contradiction ... However, the commission does not ‘prohibit’ marketers from ever using ‘synthetic.’
“It lacks a sufficient basis for doing so because the evidence does not establish that the term would be deceptive in every instance. If a marketer uses ‘synthetic’ to imply that a competitor’s lab-grown diamond is not an actual diamond, however, this would be deceptive.”
Despite the elimination of the word synthetic, Stevens said overall the new guides allow for a wider range of terms to describe lab-grown diamonds.
Before, the guides advised marketers to stick to four terms when describing man-made diamonds: laboratory-grown, laboratory-created, [manufacturer name]-created and synthetic.
Now, marketers can use the first three above as well as other terms as long as they “clearly and conspicuously convey” that stone is not a mined diamond, the FTC said.
3. The word “natural” has been removed from the FTC’s official definition of a diamond.
The FTC originally defined a diamond as “a natural mineral consisting essentially of pure carbon crystallized in the isometric system.”
The Diamond Foundry advocated for the removal of the word “natural” and the FTC agreed, writing: “When the commission first used this definition in 1956, there was only one type of diamond product on the market—natural stones mined from the earth. Since then, technological advances have made it possible to create diamonds in a laboratory. These stones have essentially the same optical, physical, and chemical properties as mined diamonds. Thus, they are diamonds.”
Yood, however, said this is not as consequential as it may seem. The FTC is essentially saying that because the definition precedes the diamond section of the guides, and since diamonds are no longer just mined, it is removing “natural” so that the guidelines that follow apply to all diamonds, whether natural or man-made.
The FTC still holds that the terms real, genuine, natural and precious cannot be used for lab-grown stones.
“So if you are using the word ‘diamond’ unqualified, you are still talking about a natural diamond,” Yood said.
Previously, Yood said, jewelry needed to be 10 karats or higher to be called gold in the United States, but that is no longer the case.
The FTC’s revised guides eliminated that threshold, meaning now 8-karat, or even 5- or 6-karat material, can be sold as gold in the U.S.
Held over, however, is the rule on karat fineness disclosure. Yood said if marketers describe jewelry simply as “gold,” then they are essentially saying it is 24-karat gold. The karat weight (14K, 18K, etc.) must be included with each piece that is not 24-karat gold.
In changing the rules, the FTC cited a 2016 Harris study that indicated a majority of consumers understand that the amount of gold in an alloy impacts its color, likelihood of tarnishing and corroding, overall durability, and resale value.
The study, “suggests most consumers will understand that a product containing less gold than traditional gold jewelry may perform differently from higher karat gold—i.e., that an 8K ring would have different color, performance, and resale value than a 14K ring,” the FTC wrote.
Regarding silver, there was a 925-parts-per-1000 minimum for sterling silver. Now, she said, there can be alloys under that amount, though a piece still has to be .925 to be called sterling silver and the fineness of the silver still has to be included with each piece, just as the karat weight of the gold does.
5. Rhodium plating must now be disclosed.
Yood said the JVC backed this change because many consumers who purchase white gold aren’t aware that it is rhodium plated, and that the plating will wear off but can easily be reapplied.
“This (change) is about consumers understanding the product they are purchasing and understanding that when it does wear away, it actually can be fixed,” she said.
6. There are now guidelines for describing what are known as composite gemstones.
Prior to the revision, the Jewelry Guides were not clear in regards to describing “composite” gems.
While the JVC is still seeking clarification on this section, what is clear is that it is no longer enough to just use the term lead glass-filled ruby.

Composite gems also cannot be described as treated or have any of the approved terms for lab-grown stones applied to them.
The FTC said the terms that are acceptable are: composite, hybrid or manufactured, as long as the terms are “effectively qualified to convey that the product does not have the same properties as the named stone and that it requires special care.”
7. “Yellow emerald” and “green amethyst” are no longer acceptable terms.
The “misrepresentation” of various varieties of minerals was another area addressed by the FTC in revising the Jewelry Guides.
Citing consumer confusion over the value of certain gemstones, the JVC pushed for, and won, a modification to the guides in which marketers are cautioned not to mark or describe a product using an incorrect varietal name.
The two examples mentioned throughout the section are “yellow emerald,” which is sometimes—but should not be—used to describe the gemstone more accurately known as golden beryl or heliodor, and “green amethyst,” which should be referred to using its correct name, prasiolite.
8. There is a new section on disclosure of treatments for pearls and cultured pearls specifically.
Under the old guides, the rules about treatment disclosure for colored gemstones—that treatments that are not permanent, need special care and/or have an effect on value—were generally applied to pearls too.
Yood said the JVC advocated for the FTC to add a separate section for pearls, and they did.
A complete version of the revised Jewelry Guides is available on the FTC’s website.
Stevens, the JVC president, said the committee is working on translating the new Jewelry Guides, which are 150-plus pages and rife with legalese, into a document that is compact and readable.
In addition, the JVC plans to hold a webinar highlighting the main changes to the guides in the future and will be speaking about them at upcoming jewelry trade shows and other jewelry events.
The Latest

Experts from India weigh in the politics, policies, and market dynamics for diamantaires to monitor in 2026 and beyond.

The American precious metals refiner’s day-to-day operations remain the same post-acquisition.

Every jeweler faces the same challenge: helping customers protect what they love. Here’s the solution designed for today’s jewelry business.

These aquamarine jewels channel the calming energy of the March birthstone.


The “Innovative Design” category and award will debut in the Spectrum division of this year’s AGTA Spectrum & Cutting Edge Awards.
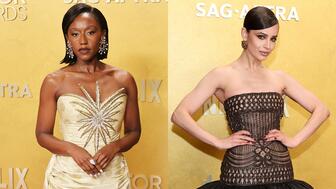
Diamond jewelry was the star of the event formerly known as the SAG Awards.
With refreshed branding, a new website, updated courses, and a pathway for growth, DCA is dedicated to supporting retail staff development.

Consumers were somewhat less worried about the future, though concerns about rising prices and politics remained.

Foerster is this year’s Stanley Schechter Award recipient.

Sponsorships and tickets to the annual fundraising event, set for May 31, are available now.

Chicago police and members of the U.S. Marshals Service tracked down the 35-year-old suspect earlier this week in St. Louis.

Owners of the Ekapa Mine reportedly filed for liquidation about a week after a mudslide trapped five workers who have yet to be found.

A 10-year alliance has also begun to address the shortage of bench jewelers through scholarships, enhanced programs, and updated equipment.

The “Splendente” collection has evolved to feature hardstone letter pendants, including our Piece of the Week, the onyx “R.”

The jewelry collection belonged to “one of society's most glamorous and beautiful women of the mid-20th century,” said the auction house.

The update came as Anglo took its third write-down on the diamond miner and marketer, which lost more than $500 million in 2025.

Emmanuel Raheb discusses the rise of “GEO” and the importance of having well-written, quality content on your website.

Each received around four years for burglarizing a jewelry store and a coffee shop in Simi Valley, California, last May.

Catherine Aulick, a GIA graduate, received the ninth and final Gianmaria Buccellati Foundation Award for Excellence in Jewelry Design.

We asked a jewelry historian, designer, bridal director, and wedding expert what’s trending in engagement rings. Here’s what they said.

Beth Gerstein discusses the vibe of the new store, what customers want when fine jewelry shopping today, and the details of “Date Night.”

Are arm bands poised to make a comeback? Has red-carpet jewelry become boring? Find out on the second episode of the “My Next Question” podcast.

The Swiss watchmaker is battling declining sales amid a rapid retail expansion, according to a Financial Times report.

The campaign celebrates Giustina Pavanello Rahaminov, the co-founder’s wife and matriarch of the family-owned brand, for her 88th birthday.

Rachel Bennett, a senior jeweler who has been with Borsheims since 2004, earned the award.

The industry veteran, who was with The Edge Retail Academy for 14 years, joins her husband at the company he founded in 2022.