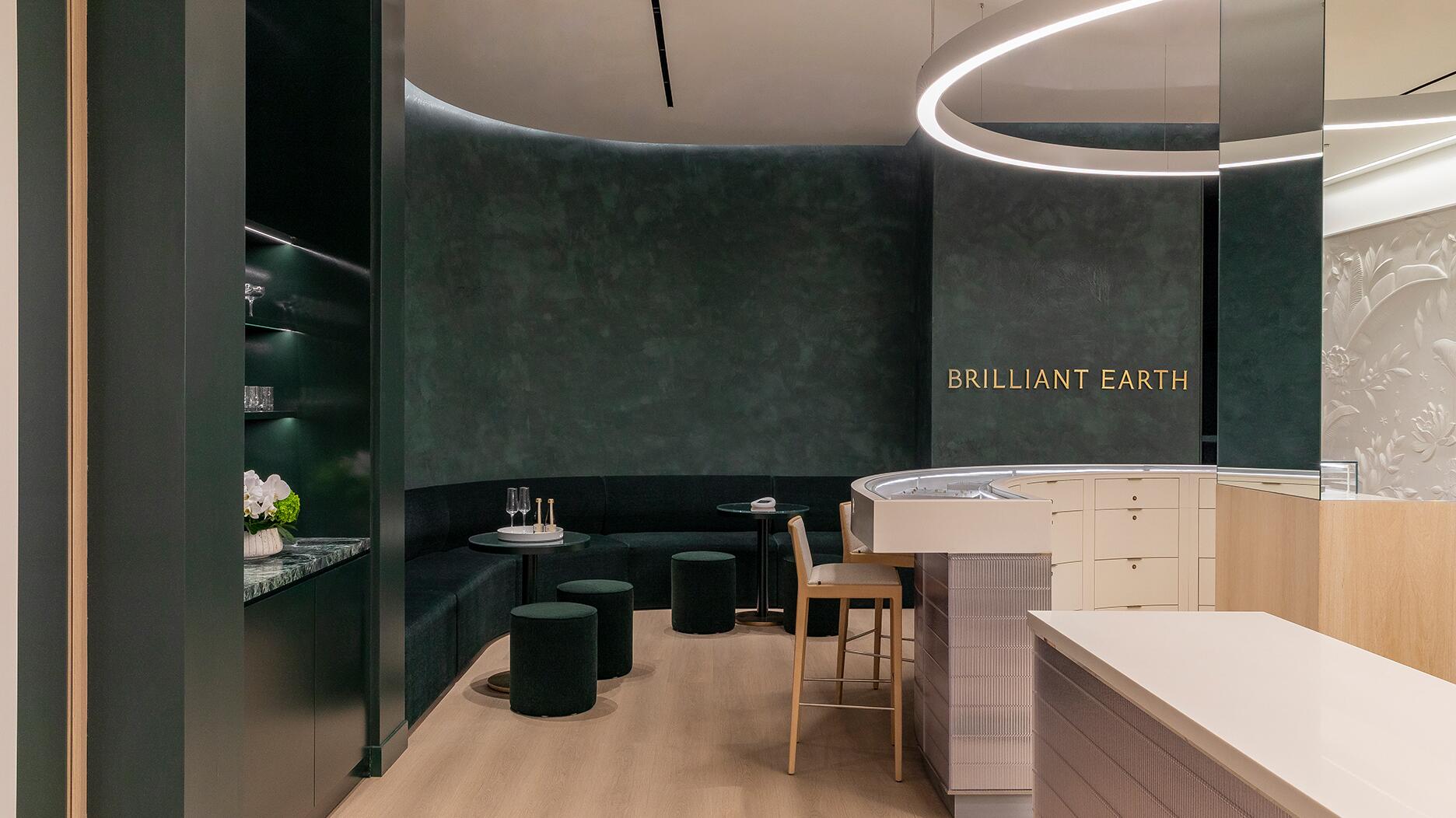
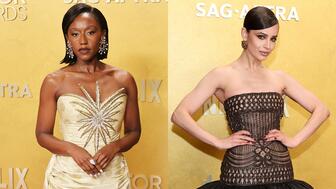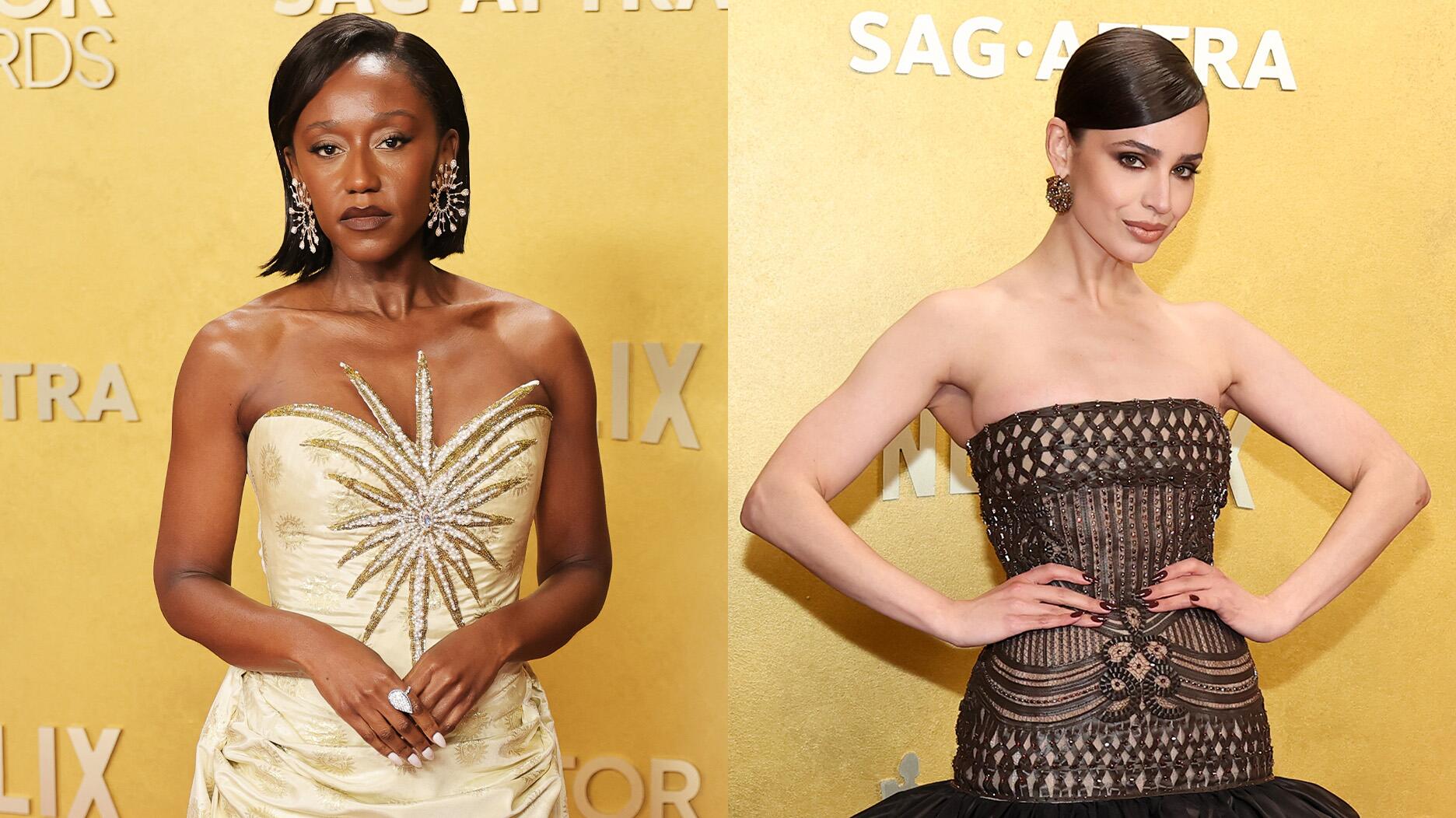Our Pieces of the Week honor the 2026 nominees for the Gem Award for Jewelry Design, Silvia Furmanovich, Cece Fein-Hughes, and Catherine Sarr.
A Quick Review of the FTC’s Rules on Lab-Grown Diamonds
Our Editor-in-Chief Michelle Graff offers a refresher following the Federal Trade Commission’s distribution of eight warning letters regarding advertisements for lab-grown diamond jewelry or diamond simulants.

The distribution of these letters comes less than a year after the commission’s long-awaited overhaul of the Jewelry Guides, the FTC-created rulebook that outlines the terms marketers should, and shouldn’t, use to describe jewelry to consumers.
When the new Jewelry Guides dropped last summer, it seemed, to me anyway, that many lab-grown diamond companies perceived the revisions to be a big victory for them, perhaps bigger than it actually was. They’ve since gone a little overboard with their marketing, either thinking that it was allowed or that nobody was watching or would notice.
But that, apparently, is not the case.
The FTC is paying attention and is interpreting the revised guides more strictly than some had expected, including Jewelers Vigilance Committee President and CEO Tiffany Stevens, whose organization is tasked with (among many other things) keeping the industry’s advertising in check.
Stevens told me in an email Thursday that, “We are extremely encouraged that the FTC is putting focus on our industry in this way at this time. The guides had not been updated since the ‘90s, and in our conversations with the FTC, we emphasized that the update really wasn’t complete until they took some enforcement action to demonstrate the meaning and limits of the new guides.
“We were seeing evidence of some players really creating their own reality and running wild beyond any reasonable interpretation of the new guides. We would reach out to stem the action and also see incidents in our mediation practice, but there is nothing like having such a loud and clear action from the federal government itself.”
All this being said, I thought in light of this week’s events, now would be a good time for a refresher on the FTC’s Jewelry Guides as they pertain to man-made diamonds and simulants.
1. If a product is a lab-grown diamond, then the fact that it is man-made must be clearly and conspicuously stated.
The FTC made the change to the definition of a diamond in its Jewelry Guides before the section on diamonds as a way of saying: We will lay out the guidelines in this coming section that apply to diamonds, and by diamonds we mean “a mineral consisting essentially of pure carbon crystallized in the isometric system” that was either mined from the earth or grown in a factory.
Nothing changed about how lab-grown diamond companies, and sellers of lab-grown diamonds, have to describe the product to consumers.
The FTC says they still must make it clear that the product is man-made by using “clear and conspicuous” disclosure with the word diamond; the three terms the FTC recommends using are laboratory-grown, laboratory-created or [manufacturer name]-created.
Cultured is OK too, but it has to be “immediately accompanied, with equal conspicuousness” by one of the three terms; it cannot stand alone.
When “diamond” appears by itself, it still means a natural diamond.
And those three qualifying terms mentioned above, the FTC noted this week, must be “proximate” to the product description, not in a place where consumers aren’t likely to see them. It mirrors the rules the commission has laid out for paid posts by influencers, who are supposed to write “#ad” where people can see it, not bury it in the middle of a caption.
Companies cannot relegate disclosures to FAQ or education pages, with FTC Consumer Education Specialist Bridget Small noting in a blog published on FTC.gov Tuesday: “Some businesses only put information about how a stone was really made on a ‘diamond education’ webpage, rather than in or near an ad where shoppers were more likely to see it.”
2. Social media is a not a free-for-all.
The FTC reminded companies that the Jewelry Guides and the truth-in-advertising provisions of the FTC Act apply on Instagram, Facebook and Twitter, too.
Frisby also urged marketers to be cautious when using hashtags, for two reasons.
First, if a marketer wants to use a hashtag for disclosure purposes—e.g., #labgrown—they have to consider the overall impression of the advertisement. Is that hashtag making it obvious enough to consumers what the product is?
Secondly, marketers need to be mindful of making claims with hashtags. For example, #diamonds might imply that a product is mined, since the FTC still considers “diamond” alone as referencing a mined diamond.
3. CZ and moissanite aren’t the same thing as diamond (either natural or man-made), and that must be clear too.
In addition to the ads for lab-grown diamonds, the FTC noted that it spotted advertising for simulated diamonds that implied the stone was either a lab-grown or mined diamond.
The commission “encourages” companies selling simulated diamonds to avoid describing their products in a way that “falsely implies” what they are selling has the same optical, physical and chemical properties as mined or lab-grown diamonds.
4. Be cautious when making “eco” claims.
For example, if a company is claiming its product is “eco-friendly” because it’s recyclable, or because it takes measures to use less energy or less water in the manufacturing process, then the ad has to state this. It can’t just state “eco-friendly” because there are too many ways consumers can interpret that.
In addition, companies need to have publicly available evidence backing up their claims, and the amount of scientific evidence that’s needed increases with certain claims, such as “carbon neutral.”
The FTC has an entire rulebook dedicated to “eco” claims, separate and apart from the Jewelry Guides. It is called the “Green Guides” and can be accessed on FTC.gov.
The JVC’s Stevens added a point I’ve made in writing about lab-grown diamonds on this blog before: a product cannot be labeled as “green” or “eco-friendly” simply because it is perceived to be “greener” than the same product next to it.
She explained it like this: “One of the recurring issues we see with the environmental claims is the use of relative standards (i.e., Michelle speaks 20 words of Spanish and Tiffany speaks one so Michelle is fluent in Spanish) rather than what the standard actually is under the [FTC’s] Green Guides, which is an absolute (i.e., Michelle is either fluent in Spanish or not, regardless of how competent the person standing next to her is.)”
Before I wrap up this blog, it’s worth noting that the FTC is not a law enforcement body; no one is going to prison for putting out diamond jewelry ads that violate the FTC’s Jewelry Guides.
However, the commission can levy fines, and, what might even be worse for these companies, the commission publicizes when it writes warning letters, which can result in coverage not just from trade press but consumer press as well.
Reuters picked up the story about the FTC’s warning letters, as did Ad Age.
The story even made it onto Page Six of the New York Post, which ran it with the headline, “Leonardo DiCaprio-backed diamond company accused of false advertising,” zeroing in on the Diamond Foundry.
The FTC is not disclosing the names of the seven other companies that received warning letters without a Freedom of Information Act request.
A spokeswoman for the Diamond Foundry said the company is limited as to what it can say at this point, but released the following statement: “We have received an inquiry from the FTC, which we take seriously and will respond to in comprehensive detail. We pride ourselves on being a lab-grown diamond producer, and this point of differentiation is what our success is built on. We have worked collaboratively with the FTC for years, and the FTC has been a great supporter of the industry and a champion of change for consumer transparency.”
The FTC is giving the companies it contacted 10 days to let the commission know how they plan to alter their advertising.
The Diamond Foundry said it will share follow-up information when available.
Stay tuned. I bet this isn’t the last we’ll hear from the FTC regarding the revised Jewelry Guides.
The Latest

The 24-piece watch collection is set to debut in spring 2027.

Pooler, who has more than 25 years’ experience in jewelry, is now chief operating officer of Modani Jewels, Soham Diamonds, and SNJ Creations.

Every jeweler faces the same challenge: helping customers protect what they love. Here’s the solution designed for today’s jewelry business.

The reopening of the Waldorf Astoria means a homecoming for the industry group’s annual event, which will take place Saturday.


McCormack looked to the 19th century’s “golden age” of astronomy when designing her new celestial-themed collection.

Nelson will be honored as the inaugural grant winner at the Gem Awards gala on Friday.
With refreshed branding, a new website, updated courses, and a pathway for growth, DCA is dedicated to supporting retail staff development.

The new smart design software allows jewelers to configure, price, and confirm a custom engagement ring in real time for in-store customers.

The 10,000-square-foot diamond manufacturing facility officially opened in late February and employs 50 people.

The MJSA Education Foundation’s scholarships support students pursuing jewelry careers.

The largest white diamond to come to market in the U.K. in more than a decade, the VVS1, I-color stone is expected to top $1 million.

Skelly shares her plans for reimagining the fine jewelry retailer she re-acquired after it faltered last year.

The collection takes inspiration from the emotional space between people, moments, and experiences.

In 2026, the jewelry retailer is celebrating a milestone only a small percentage of family-owned businesses survive to see.

The group of jewelers held a jewelry raffle in support of the Children’s Hospital of Richmond at VCU.

The jewelry giant released preliminary results for the fourth quarter and full year on Monday, with final results slated to come next week.

The retailer also gave an update on its vendor partnerships.

The award-winning actress is the “epitome of modern allure,” the brand said.

The “Bloom” collection draws from the flower power movement of the 1960s and ‘70s with inlay pendants offered in eight colorways.

The unique piece was one of the custom works offered at the foundation's recent silent art auction, which garnered nearly $15,000 in total.

Bulgari named Gyllenhaal as its brand ambassador for his embodiment of artistic depth, intellectual curiosity, and warmth.

Awards were given to four students, one apprentice, and an emerging jeweler.

The top jewelry lot of the late model’s estate sale, hosted by John Moran Auctioneers, was an Oscar Heyman & Brothers for Cartier necklace.
Moses, who started at GIA’s Santa Monica lab in 1976, will leave the Gemological Institute of America in May.

Increased competition, falling lab-grown diamond and moissanite prices, and the rising cost of gold took a toll on the moissanite maker.

The earrings, our Piece of the Week, feature pink tourmalines as planets orbiting around an aquamarine center set in 18-karat rose gold.