In a 6-3 ruling, the court said the president exceeded his authority when imposing sweeping tariffs under IEEPA.
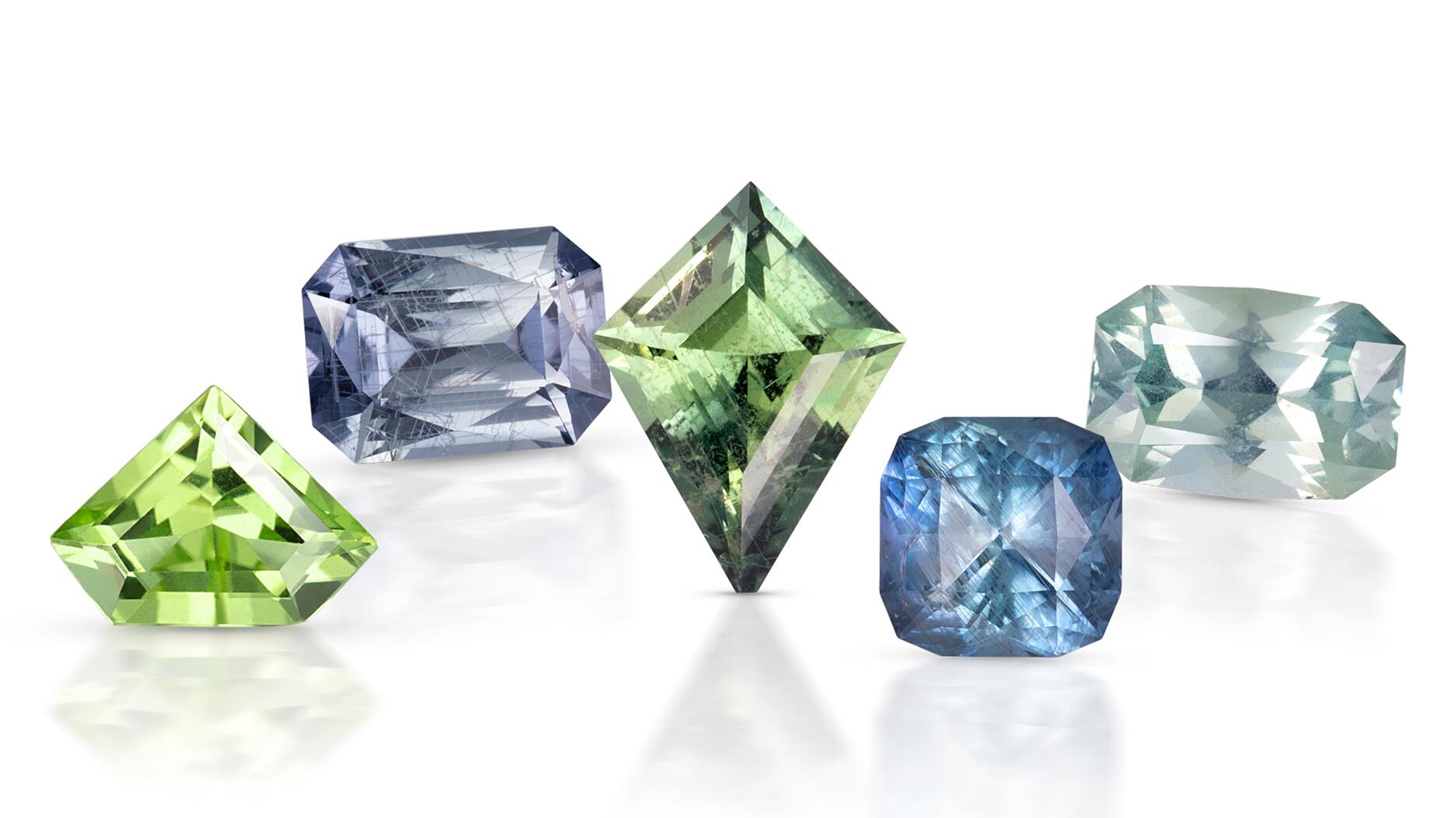
State of the Colored Stone Market: Building Benefits at Home
More source countries are moving to keep the value of their mineral resources in country. What does this mean for the colored stone sector both locally and around the globe?

Colored gemstone source countries have begun taking more control of their mineral wealth in order to retain more value.

For most, the movement stems from knowing their governments and their communities haven’t been reaping the benefits of their lands’ natural resources at the level they should be.
“I think the main driver is the realization in the governments of some of these countries that there’s been a huge disparity between the value of their resource once it leaves their border and the benefit that it’s brought, or really, the lack of benefit the resources have brought to the local populations,” says Gemworld International’s Stuart Robertson.
Regulations to build beneficiation in-country aren’t exactly new—laws and initiatives to capture more revenue come and go—but there appear to be increased efforts in several places over the past few years.
They’re taking different forms: new duties, royalties and fees; laws aimed at controlling mining; limits on exports with the intention of developing cutting and manufacturing sectors within the communities; and education programs.
These beneficiation initiatives’ end goal seems simple at first blush—to ensure that these resources are going back to the producing communities. But what happens in-country is actually complex and can create challenges along the way.
The Changing Market in Tanzania
East Africa is, arguably, the colored stone industry’s most important region right now, producing a large quantity of goods and showing the most potential for new mines.
This is especially true of Tanzania. The country is currently the source of dozens of types of gem-related materials, according to Robertson, so when its government started passing laws to tighten control of the mining and export of gems, the gem world took notice.
More than a decade ago, in a move to create jobs and retain value from its natural resources, the Tanzanian government banned the export of any tanzanite rough weighing more than 1 gram (5 carats), requiring it to be cut in country.
In 2017, President John Magufuli ordered construction of a wall around the tanzanite mines in Merelani after an investigation led officials to believe some mining firms were smuggling stones out and dodging taxes, according to local news reports.
While some wondered about the effectiveness of this wall in preventing smuggling, Robertson says its construction sent a clear message that the government is serious about taking control of its resources.
For some time last year, no rough stones could be exported from Tanzania.
Then earlier this year, the Tanzanian government eased up a bit, banning only the export of six minerals—ruby, sapphire, emerald, any type of green garnet and spinel—weighing more than more than 2 grams (10 carats).
Rough over that weight has to be cut in country; everything under can be exported, according to gemstone faceter Roger Dery, who travels to the country regularly to source gemstones.
The country also has been adjusting the royalties applied to the value of exports and adding fees.
In Tanzania, it costs $100 to purchase an export license. Exporters also must pay a 6 percent royalty on the value of rough stones leaving Tanzania and 2 percent on cut stones (these are reduced export royalties after feedback from the industry that recent hikes were too high, according to Robertson, but are still up slightly from last year.)
There’s also a 1 percent fee that goes to the Ministry of Minerals for processing packages.
In the gem-trading area of Arusha, government officials also have gotten stricter about enforcing the requirement that foreign buyers have a business visa to operate, Dery says. It costs $250.
Peter Periera, a dealer based in Tanzania who also operates a cutting center and used to be a miner, says the taxes are more streamlined now, and though they could be lower, the gem industry in the country “can work with that.”
He did note, though, the $100 export license is hard for many locals to buy. He estimates 80 percent of brokers who work directly with miners can’t afford the new fee structure.
This means more miners have to travel to take their goods to market or more people opt into “quietly buying on the side” to avoid taxes.
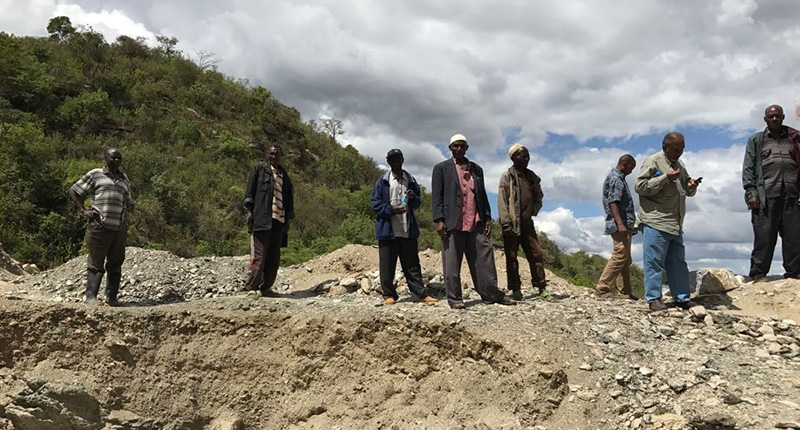

Another big change in the market—President Magufuli decided last year the government would build gem centers throughout the country, offering facilities for trade and export activities.
The goal, as of now, is to have one in each of Tanzania’s 20 regions, though not every region has gem material, so it remains to be seen if that will be the case.
While these regional gem centers could open the market to more international buyers, they’re not without their issues.
The government finished its first gem center in May, choosing to open the inaugural location in Namanga, which sits on the Tanzania-Kenya border, to test the system. It created some struggles at first since it’s not the most central location and is about 110 kilometers (68 miles) from Arusha, where much of the country’s trade occurs.
But the government followed Namanga with a second gem center in Arusha, which is now operational.
Periera brings up another gripe about the gem centers—they are forcing everyone to sell in the same place, which presents problems for small miners. He says they don’t necessarily want others to know how much they’re producing or how much money they have because it presents a security issue.
It also means more competition for miners—if they are able to travel to the gem centers at all—as buyers can look around before they purchase.
All these changes are intended to help the Tanzanian government more closely regulate its mineral resources and retain more of their value.
While many agree that the idea behind it is positive in the long run, the scale of changes made in a relatively short span of time hasn’t made things easy for the trade.
“I think it’s creating frustration for the Tanzanians because it’s a moving target,” Dery says. “You might set up your business to operate in a particular way based on government regulation, then six months in you’re doing it a different way.
“If you’ve been at something for only three or four months, you can probably adjust on the fly. But if you’ve been doing something for 20 years and the government says you can’t do it that way anymore, you might have a whole business structure built on what you thought was going to be permanent.”
Dery also says the ban on rough exports hasn’t done much to create more work for the country’s estimated 650-700 gem cutters, from what he’s seen and heard. He estimates that the number of cutters and the amount of rough have balanced out.
But, “10 years from now, if they have another 600-800 gem cutters who are trained on modern machines, I think you’re going to have an escalation in revenue and people choosing that location as a place not just to buy, but a place to take their goods to be cut.”
Periera says even though he sees the lower 2 percent duty on faceted stones encouraging cutting in Tanzania, the country’s cutting sector isn’t established enough to handle the material on the market now.
“They’re not yet capable of cutting all the material that we require. We’re a long way out. It’s impossible at the moment.”
However, he says that at the end of the day, the new regulations and duties will be for the best.
“It’s a step forward. At the moment, it’s kind of a rough patch; a very rough patch. But I think with time, all the wrinkles will get ironed out and in the future it will get smoother.”
Dery agrees, noting that while the government should consider being less restrictive to allow commerce to occur, having the regulations in place isn’t necessarily a bad thing: “They [the Tanzanian government] had to start somewhere. It might’ve been uncomfortable, but they had to start somewhere.”
And the changes have shown some monetary benefits.
According to local reports, tanzanite revenues rose to approximately $461,000 in September 2018, up from a low of about $74,000 in January 2015.
Tanzania’s government says the mining sector contributes about 5 percent to the country’s GDP. Under Tanzania’s “Development Vision 2025” plan, it’s expected to account for 10 percent in the coming years.
“If the situation in Tanzania proves to see a benefit—let’s say by 2025 they get to 10 percent of the GDP coming from the mineral resources sector—then you’re going to see most of their neighbors take notice of that and start to put in similar types of regulations,” Gemworld’s Robertson says.
[National Jeweler reached out to Tanzania’s Ministry of Minerals for comment on this story but did not receive a reply by deadline.]
Ethiopia Finding Its Way
One of those neighbors, Ethiopia, has already started.
This might not be surprising to anyone watching the supply side of colored stones. The 2016 discovery of emeralds in Shakiso refocused attention on the country.
According to Hewan Zewdi, co-founder of Seattle-based Agere Treasures LLC, who travels to Ethiopia and sources directly from miners, the government is taking its time to learn from other countries and is engaging the country’s gemstone community for feedback as it develops new rules.
Under consideration is one requiring exporters to receive some gemological education in order to obtain an export license so they have an idea of the value of stones they’re selling.
This hasn’t been enacted as of press time, and Zewdi says it’s unclear at this time how the country would support such a requirement. The government has indicated it may do this by providing an online program or creating local training programs.
And while Ethiopia currently only has restrictions on the export of opal—a minimum of 40 percent of material exported must be cut and polished, while a maximum of 60 percent can be exported as rough—rather than a larger gemstone ban, Zewdi says the government is limiting the number of export licenses it gives to foreigners.
The Ministry of Mines has set a minimum price on gems to be exported based on quality; this is done, she says, to create an average price to protect the economy and prevent exporters from selling below value.
“If the situation in Tanzania proves to see a benefit—let’s say by 2025 they get to 10 percent of the GDP coming from the mineral resources sector—then you’re going to see most of their neighbors take notice and start to put in similar types of regulations.” — Stuart Robertson, Gemworld International
The Ethiopian government also has opened more than a dozen new lapidary institutions to train cutters and wants to grow its jewelry making businesses.
It also wants to encourage mining education.
As is the case in many source countries, miners in Ethiopia often can’t afford the time or money to travel to the cities where gem trading takes place and so they rely on brokers, Zewdi says. The brokers then sell in the cities, where they charge much higher prices than what they paid at the mine.
The Ethiopian government wants to educate miners about the gem material so they better understand the value of their stones and what they should charge, similar to how the Gemological Institute of America developed a gem guide for small-scale miners in Tanzania and trained them on the ground.
Overall, Zewdi says the country is “moving in a good direction” and going about it in the right way. The government understands the need to collaborate with locals and mining associations so regulations don’t stifle the market, which is especially important for a country trying find its place in the international market.
Myanmar Rebuilds a Historic Market
Myanmar’s gem sector has a long, complicated history.
The country’s rubies are among the most sought-after in the world, but its colored stones are inextricably linked to its political system—having long brought wealth for its leaders with ties to the gem sector, some of whom forced their way into power—and, as a result, gems have been the focus of government control and foreign sanctions.
But, just as is happening in East Africa, Myanmar’s leaders have realized the country could make more money from its resources so they too are enacting change designed to build beneficiation, tighten distribution and clean up mines.
The Natural Resource Governance Institute, or NRGI, is an international nonprofit that works to improve the governance of natural resources in a variety of countries to promote sustainable and inclusive development.
NRGI has been engaging with governmental body Myanmar Gems Enterprise to improve transparency mechanisms, like collaborating to launch OpenJadeData.org, helping with an internal information management system for licensing, improving tax capture from the sector and drafting gemstone policy. It also provides commentary on already developed laws.
According to Maw Htun Aung, Myanmar country manager at NRGI, the government enacted a new law in January aimed primarily at more sustainable mining by addressing some of the issues that exist in its gemstone industry, such as dangerous and environmentally damaging mining methods.
In mid-2016, the country put a moratorium on issuing mining licenses for all gemstones, but given the law that just passed, Aung says they expect the government to lift the ban in late 2019 or early 2020, since the new law is intended to regulate mining so closely.
What’s important for the country right now, Aung says, is buildings its infrastructure.
Beneficiation and, specifically, value addition haven’t really been developed in Myanmar, which he attributes to smuggling and a high tax rate, among other factors. (In Myanmar, it is illegal to export loose stones, rough or cut.)
With the new law, the government wants to attract investment in the colored stone sector to create more jobs and bring more cutting, manufacturing and even designing to the country. It needs to focus on technology to make that happen, Aung says, including technology to heat-treat more stones in the country or a government-recognized lab system to provide assurance on gems.
“It’s impossible for the government to outright make a policy that every stone should be cut and polished and processed here,” Aung says. “That’s just too ambitious, and it’s not realistic.”
NRGI also is proposing a review of the gemstone sector’s entire fiscal structure, including how to streamline the sales process. There currently are several taxes and fees in place, including a 10 percent royalty on produced stones, according to Aung.
Traders can sell at government-run gem emporiums, but “excessive fees and taxes” during the process make them unattractive to some in the sector, according to Aung.
“It’s like a punishing ground for traders,” he says.
All this is to say: The NRGI thinks it’s important for the future of Myanmar’s gemstone industry for the government to find a way to streamline and simplify the sales process, as well as possibly decentralize it by building gem centers outside of the capital.
What’s more, how the government interprets and enacts the law—and how that will develop, or discourage, the country’s gemstone sector—remains to be seen. Much will depend on the Myanmar Gems Enterprise body, Aung says.
While he says he doesn’t see Myanmar departing radically from the existing model, what’s different is for the first time, the government is holding multi-stakeholder dialogue with the industry, civil society and the community.
But the question remains: Is it too little, too late? Aung worries this may be so.
He says reforms should’ve happened a decade ago, noting the country is at a stage where its mining sector has become notorious for all the wrong reasons—unsafe practices, smuggling and human rights issues such as, most recently, its stones being dubbed “genocide gems” for their link to the persecution of the country’s Rohingya Muslim population—and might be too far gone.
GemWorld International’s Robertson doesn’t think it is too little too late, but agrees the reforms in Myanmar are coming at a time when gem production in the country is much smaller than it used to be.
[Myanmar Gems Enterprise did not respond to an email request for an interview by deadline.]
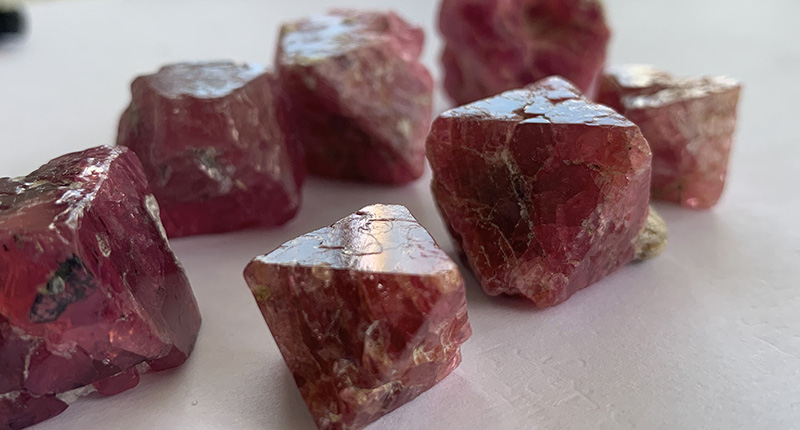

The Ripple Effects
While some of the changes these gemstone mining countries are making cause immediate growing pains, any benefits likely will take a while to become evident.
The NRGI’s Aung says it likely will be at least a decade before Myanmar builds enough of an infrastructure to support a market that would allow the country to compete and benefit.
The Tanzania-based gem dealer Periera, too, thinks it will take his country a while to smooth out the kinks in the system so that it lets the market operate in the best way possible.
After all, the changes that must occur are long-term considerations, which can be hard to maintain, American Gem Trade Association CEO Doug Hucker asserts.
“Everything that you need to produce value-added economies is lacking in most emerging countries—a sophisticated civil society, a transparent regulatory community that oversees gemstones, access to education,” he says. “There are dozens of people who are doing this to a minor extent, working to improve the community where they are extracting these materials. But in most cases, much more effort needs to be devoted to teaching the local people how to take advantage of the skills they can develop.”
But if there’s no market for that material, he adds, none of that will matter.
“What most of these countries need is cooperation … the education that we can provide, the financial support and the access to a marketplace.”
Hucker also believes that due to the decentralized nature of the colored gemstone industry—it is not organized and supported by a few big mining companies in the same way as, say, the diamond industry—it needs to take small steps to help develop marketplaces for local producers and manufacturers in many countries.
These small steps are already being taken in several countries, such as in Kenya, which has built a gem center in Voi, a facility that will offer identification, faceting, trading opportunities, fairs and training—once it is open.
The country has also been pushing the Kenya Gem & Jewellery Fair in Nairobi in partnership with the Association for Women in Energy and Extractives in Kenya, showcasing colored stones and providing educational and networking opportunities.
There are also programs like gem dealer Tom Cushman’s gemological school in Madagascar, or Columbia Gem House’s Fair Trade Gems protocols that support local production at the mines where it sources, such as in Malawi, through sales, development projects and critical needs in the local communities.
“Whether it’s the industry itself or it is the country, there has to be a cooperative effort to look at this and say, how do we develop regulatory schemes that actually work?” Hucker says.
As each country adjusts to its new normal, the changes are bound to have ripple effects throughout the international market.
Gemworld’s Robertson says the moves toward increased beneficiation for countries will change distribution channels, shortening them a bit as some middlemen are cut out, especially in Tanzania.
As a result, price increases are likely, especially for higher-quality stones, he adds.
However, he thinks the market will embrace and absorb the increases and changes, not only because it has to but also because it’s the right direction to move in given current consumer interest in social responsibility and responsible sourcing.
“I think, in general, the market will embrace these things because more and more people are becoming aware of the huge disparity in wealth between the retail end of the market and some of these producing nations,” concludes Robertson.
The Latest

Smith encourages salespeople to ask customers questions that elicit the release of oxytocin, the brain’s “feel-good” chemical.

JVC also announced the election of five new board members.

Launched in 2023, the program will help the passing of knowledge between generations and alleviate the shortage of bench jewelers.

The brooch, our Piece of the Week, shows the chromatic spectrum through a holographic coating on rock crystal.


Raised in an orphanage, Bailey was 18 when she met her husband, Clyde. They opened their North Carolina jewelry store in 1948.

Material Good is celebrating its 10th anniversary as it opens its new store in the Back Bay neighborhood of Boston.

Criminals are using cell jammers to disable alarms, but new technology like JamAlert™ can stop them.

The show will be held March 26-30 at the Miami Beach Convention Center.

The estate of the model, philanthropist, and ex-wife of Johnny Carson has signed statement jewels up for sale at John Moran Auctioneers.

Are arm bands poised to make a comeback? Has red-carpet jewelry become boring? Find out on the second episode of the “My Next Question” podcast.

It will lead distribution in North America for Graziella Braccialini's new gold pieces, which it said are 50 percent lighter.

The organization is seeking a new executive director to lead it into its next phase of strategic growth and industry influence.

The nonprofit will present a live, two-hour introductory course on building confidence when selling colored gemstones.

Western wear continues to trend in the Year of the Fire Horse and along with it, horse and horseshoe motifs in jewelry.

Rossman, who advised GIA for more than 50 years, is remembered for his passion and dedication to the field of gemology.

Guthrie, the mother of “Today” show host Savannah Guthrie, was abducted just as the Tucson gem shows were starting.

Butterfield Jewelers in Albuquerque, New Mexico, is preparing to close as members of the Butterfield family head into retirement.

Paul Morelli’s “Rosebud” necklace, our Piece of the Week, uses 18-karat rose, green, and white gold to turn the symbol of love into jewelry.

The nonprofit has welcomed four new grantees for 2026.

Parent company Saks Global is also closing nearly all Saks Off 5th locations, a Neiman Marcus store, and 14 personal styling suites.

It is believed the 24-karat heart-shaped enameled pendant was made for an event marking the betrothal of Princess Mary in 1518.

The “Kering Generation Award x Jewelry” returns for its second year with “Second Chance, First Choice” as its theme.

Sourced by For Future Reference Vintage, the yellow gold ring has a round center stone surrounded by step-cut sapphires.

The clothing and accessories chain announced last month it would be closing all of its stores.

The “Zales x Sweethearts” collection features three mystery heart charms engraved with classic sayings seen on the Valentine’s Day candies.

The event will include panel discussions, hands-on demonstrations of new digital manufacturing tools, and a jewelry design contest.