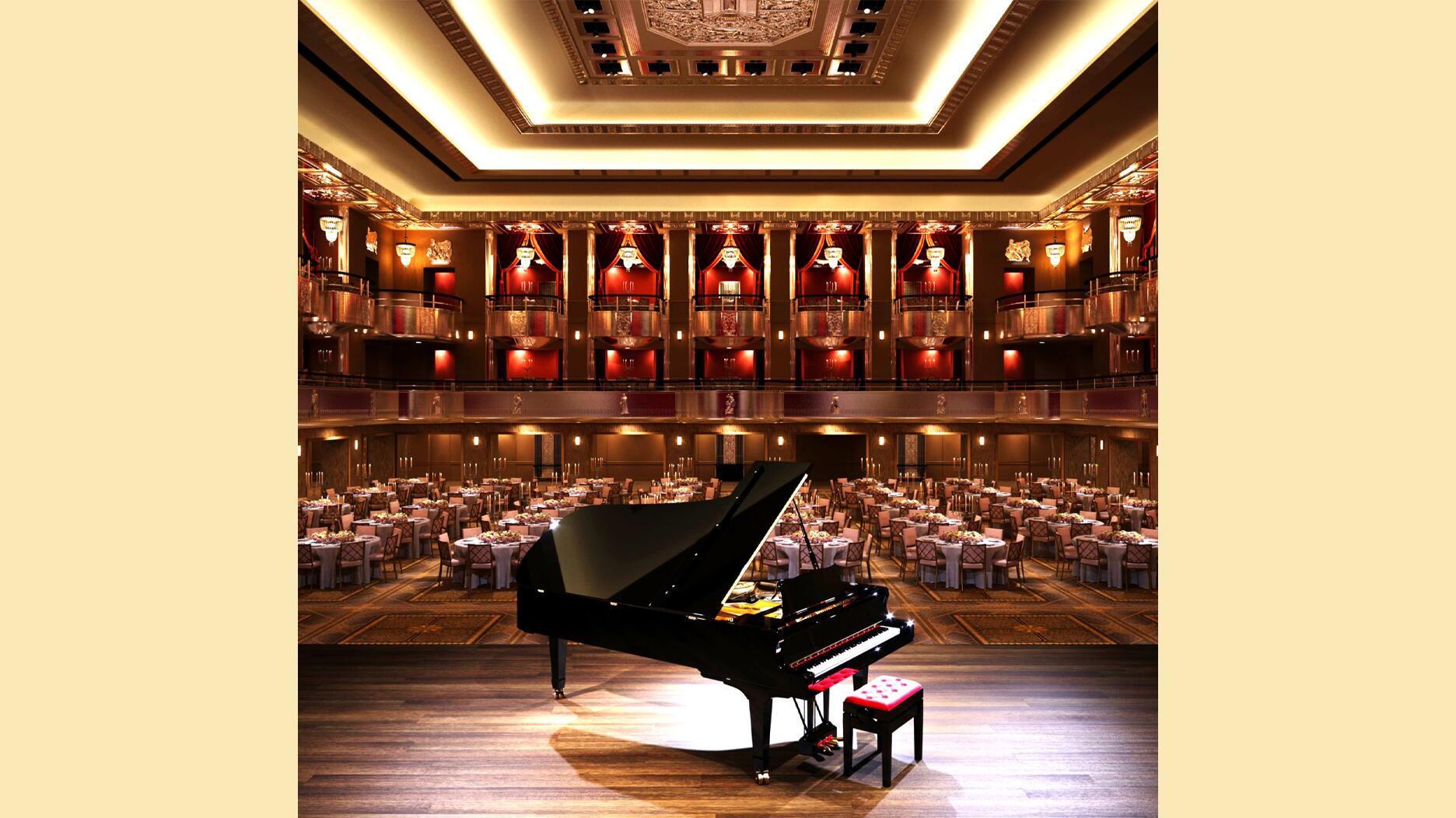
Our Pieces of the Week honor the 2026 nominees for the Gem Award for Jewelry Design, Silvia Furmanovich, Cece Fein-Hughes, and Catherine Sarr.
Analysis: Why Tiffany Won $15M from Costco
Attorneys Emily Miao and Daniel Organ dissect the jury’s verdict in Tiffany’s trademark lawsuit against wholesale club Costco.

In a highly publicized decision last year1, federal Judge Laura Taylor Swain of the Southern District of New York ruled in favor of the luxury retailer Tiffany & Co. (“Tiffany”), deciding that Costco Wholesale Corp. (“Costco”), the largest U.S. warehouse club chain, willfully infringed Tiffany’s trademark.
According to the court, Costco sold counterfeit diamond engagement rings bearing the Tiffany name and confused relevant consumers by using the word “Tiffany” in display case signage. Judge Swain’s initial ruling against Costco allowed Tiffany to take Costco before a jury to seek damages, including profits from Costco’s sale of diamond rings, statutory damages, and punitive damages.
After several delays, the jury met in September for “Phase I” of the trial to decide (1) the amount of Costco’s profits and statutory damages under the Federal Lanham Act, and (2) whether Tiffany was entitled to punitive damages under New York General Business Law §349 and New York Common Law. “Phase II” was triggered when the jury found Costco liable for punitive damages. In their Phase I verdict, the Jury determined that Costco profited by $3.7 million from the infringing sales, and added an additional $1.8 million to fully compensate Tiffany, bringing the total award for profits to $5.5 million.2 The jury also awarded $2 million for statutory damages.3 The jury further held that Tiffany was entitled to punitive damages, and in the Phase II verdict awarded Tiffany another $8.25 million.4
Analysis of Costco’s Profits
Tiffany sought an accounting of profits based on the sale of both “non-subject goods” (e.g., Costco memberships and goods other than diamond rings) and “subject goods” (e.g., diamond rings). Under Second Circuit law, in calculating “defendant’s profits,” a court should base its analysis on “infringing sales,” or sales that can be tied to the Lanham Act violation alleged.5 The court held that Tiffany presented no evidence tying the “non-subject goods” to Costco’s alleged infringement, and therefore removed the “non-subject goods” from the analysis. Regarding the “subject goods,” however, the court held that Costco did not act in good faith and therefore Tiffany was allowed to seek an accounting for profits from their sale.6 The court’s decision allowed the jury to decide, in the damages phase of the trial, how much Tiffany was entitled to for damages from Costco’s unlawful use of Tiffany’s mark.
During the damages trial, Tiffany argued that it was entitled to millions in damages from
Analysis of Statutory Damages
In addition to awarding Tiffany Costco’s profits, the jury awarded Tiffany $2 million in statutory damages. The Federal Lanham Act states that when a counterfeit mark is used, up to $2 million may be awarded for a willful violation.8 In Judge Swain’s initial ruling, the court held that, as a matter of law, Costco used a counterfeit mark and that Tiffany satisfied the willfulness requirement.9 Then, to decide the exact amount of damages, the jury was instructed to consider factors such as Costco’s profits, Tiffany’s lost revenue, and the value of the mark.10 As a result, the jury determined that the maximum $2 million in statutory damages was justified.
Analysis of Punitive Damage
Tiffany sought punitive damages under both federal and state law. Under federal law, the court held that the Lanham Act prevents the collection of punitive damages.11 Under state law, however, the court noted that New York General Business Law §349 and New York Common Law allow punitive damages, albeit with an exceptionally high bar.12 Under these laws, “punitive damages are available where a defendant’s conduct has constituted gross, wanton or willful fraud or other morally culpable conduct to an extreme degree.”13 The court listed evidence in Tiffany’s favor, including emails from Costco jewelry buyers asking vendors to copy Tiffany designs and testimony that Costco employees were aware of customer confusion but did nothing to remedy it.14
The jury ultimately agreed with Tiffany and in “Phase II” of the damages trial awarded Tiffany $8.25 million.
Conclusion
After the initial ruling, Judge Swain directed Tiffany and Costco to attempt to settle the outstanding issues. But since no settlement occurred, the damages phase proceeded and the jury handed Tiffany a sweeping victory, awarding nearly $16 million in damages.
Tiffany has been involved for many years in lawsuits regarding its intellectual property. A recent PACER search (PACER is a service for publically accessing court records electronically) returned 28 lawsuits since 1991 involving Tiffany copyrights, patents and trademarks. While the award of nearly $16 million against Costco is one of Tiffany’s largest, Tiffany previously won a default judgment of $26.5 million against numerous defendants for infringing on Tiffany trademarks and using infringing domain names.
Costco is also no stranger to lawsuits regarding intellectual property issues, both as a plaintiff and (more often) as a defendant. A recent PACER search returned 190 lawsuits over intellectual property issues since 1991, comprising 47 trademark suits of which Costco was a defendant in 36; 119 patent suits of which Costco was a defendant in 102; and 24 copyright suits of which Costco was a defendant in 22.
Tiffany has a history of policing its trademarks,15 in particular regarding goods such as its jewelry16, blue gift boxes, cufflinks, and money clips17. But Tiffany has not policed its marks with respect to engagement rings--until now. The facts here were straight forward and favorable to Tiffany, so it is unsurprising that Tiffany won. Had Tiffany lost, there would have been inherent confusion around the use of the “TIFFANY” mark as applied to diamond rings and ring settings. Such a result would have been contrary to one of the purposes of trademark protection, which is to avoid consumer confusion.18
With the conclusion of the damages trial, and assuming Judge Swain accepts the jury’s findings, Costco will likely file an appeal against Judge Swain’s ruling and the damages award. Stay tuned for further developments.
©2016 McDonnell Boehnen Hulbert & Berghoff LLP. The information contained in this article reflects the understanding and opinions of the authors and is provided for informational purposes only. It is not intended to and does not represent legal advice. No attorney-client relationship is created by providing this information to you. The information in this article is not a substitute for obtaining legal advice from an attorney licensed in your particular state.
1 Tiffany and Co. v. Costco Wholesale Corp., 127 F. Supp. 3d 241 (S.D.N.Y. Sept. 8, 2015).
2 Jury Verdict Form at 1, Tiffany and Co. v. Costco Wholesale Corp., No. 13CV1041 (S.D.N.Y. Sept. 30, 2016), ECF No. 353.
3 Id. at 2.
4 Jury Verdict Form at 1, Tiffany and Co. v. Costco Wholesale Corp., No. 13CV1041 (S.D.N.Y. Oct. 5, 2016), ECF No. 357.
5 Tiffany and Co. v. Costco Wholesale Corp., 127 F. Supp. 3d at 259 (referencing Am. Honda Motor Co. v. Two Wheel Corp., 918 F.2d 1060, 1063-64 (2d Cir. 1990)).
6 Id. at *261.
7 Tiffany's Damages Case A Publicity Stunt, Costco Tells Jury, Law360 (Sept. 28, 2016), http://www.law360.com/articles/845762/tiffany-s-damages-case-a-publicity-stunt-costco-tells-jury.
8 15 U.S.C.S. § 1117(c)(2).
9 Tiffany and Co. v. Costco Wholesale Corp., 127 F. Supp. 3d at 255.
10 Jury Instructions at 23-24, Tiffany and Co. v. Costco Wholesale Corp., No. 13CV1041 (S.D.N.Y. Sept. 30, 2016), ECF No. 345.
11 Tiffany and Co. v. Costco Wholesale Corp., 127 F. Supp. 3d at 261.
12 Id.
13 Id., (citing Altadis U.S.A., Inc. v. Monte Cristi de Tabacos, c.x.a., No. 96CV4209-BSJ, 2001 U.S. Dist. LEXIS 6892 (S.D.N.Y. May 17, 2001)).
14 Id. at 262.
15 For example, in 2006, Tiffany had an employee dedicate to monitoring listings on the eBay website for counterfeits and report any violations to eBay on a daily basis. See Tiffany (NJ) Inc. v. eBay, Inc., 576 F. Supp. 2d 463, 484 (S.D.N.Y. 2008) aff'd in part, rev'd in part sub nom. Tiffany (NJ) Inc. v. eBay Inc., 600 F.3d 93 (2d Cir. 2010) (holding that eBay did not infringe Tiffany’s marks). See also Complaint at ¶ 17 (describing other brand protection strategies).
16 See Tiffany (NJ) Inc. v. Luban, 282 F. Supp. 2d 123, 124 (S.D.N.Y. 2003) (finding the operator of a website that sold counterfeit Tiffany jewelry liable for willful infringement).
17 See Tiffany (NJ), LLC v. 925LY.Com, 2:11-CV-00590-LDG, 2011 WL 2118634 (D. Nev. May 25, 2011) (issuing a preliminary injunction in favor of Tiffany).
18 See Two Pesos, Inc. v. Taco Cabana, Inc., 505 U.S. 763, 774 (1992).
The Latest

The 24-piece watch collection is set to debut in spring 2027.

Pooler, who has more than 25 years’ experience in jewelry, is now chief operating officer of Modani Jewels, Soham Diamonds, and SNJ Creations.

Every jeweler faces the same challenge: helping customers protect what they love. Here’s the solution designed for today’s jewelry business.

McCormack looked to the 19th century’s “golden age” of astronomy when designing her new celestial-themed collection.


Nelson will be honored as the inaugural grant winner at the Gem Awards gala on Friday.

The new smart design software allows jewelers to configure, price, and confirm a custom engagement ring in real time for in-store customers.
With refreshed branding, a new website, updated courses, and a pathway for growth, DCA is dedicated to supporting retail staff development.

The 10,000-square-foot diamond manufacturing facility officially opened in late February and employs 50 people.

The MJSA Education Foundation’s scholarships support students pursuing jewelry careers.

The largest white diamond to come to market in the U.K. in more than a decade, the VVS1, I-color stone is expected to top $1 million.

Skelly shares her plans for reimagining the fine jewelry retailer she re-acquired after it faltered last year.

The collection takes inspiration from the emotional space between people, moments, and experiences.

In 2026, the jewelry retailer is celebrating a milestone only a small percentage of family-owned businesses survive to see.

The group of jewelers held a jewelry raffle in support of the Children’s Hospital of Richmond at VCU.

The jewelry giant released preliminary results for the fourth quarter and full year on Monday, with final results slated to come next week.

The award-winning actress is the “epitome of modern allure,” the brand said.

The “Bloom” collection draws from the flower power movement of the 1960s and ‘70s with inlay pendants offered in eight colorways.

The unique piece was one of the custom works offered at the foundation's recent silent art auction, which garnered nearly $15,000 in total.

Bulgari named Gyllenhaal as its brand ambassador for his embodiment of artistic depth, intellectual curiosity, and warmth.

Awards were given to four students, one apprentice, and an emerging jeweler.

The top jewelry lot of the late model’s estate sale, hosted by John Moran Auctioneers, was an Oscar Heyman & Brothers for Cartier necklace.
Moses, who started at GIA’s Santa Monica lab in 1976, will leave the Gemological Institute of America in May.

Increased competition, falling lab-grown diamond and moissanite prices, and the rising cost of gold took a toll on the moissanite maker.

The earrings, our Piece of the Week, feature pink tourmalines as planets orbiting around an aquamarine center set in 18-karat rose gold.

“The Price of Freedom” campaign video for International Women’s Day confronts the quiet violence of financial control.

Also, a federal judge has ordered that companies that paid tariffs implemented under the IEEPA are entitled to refunds.