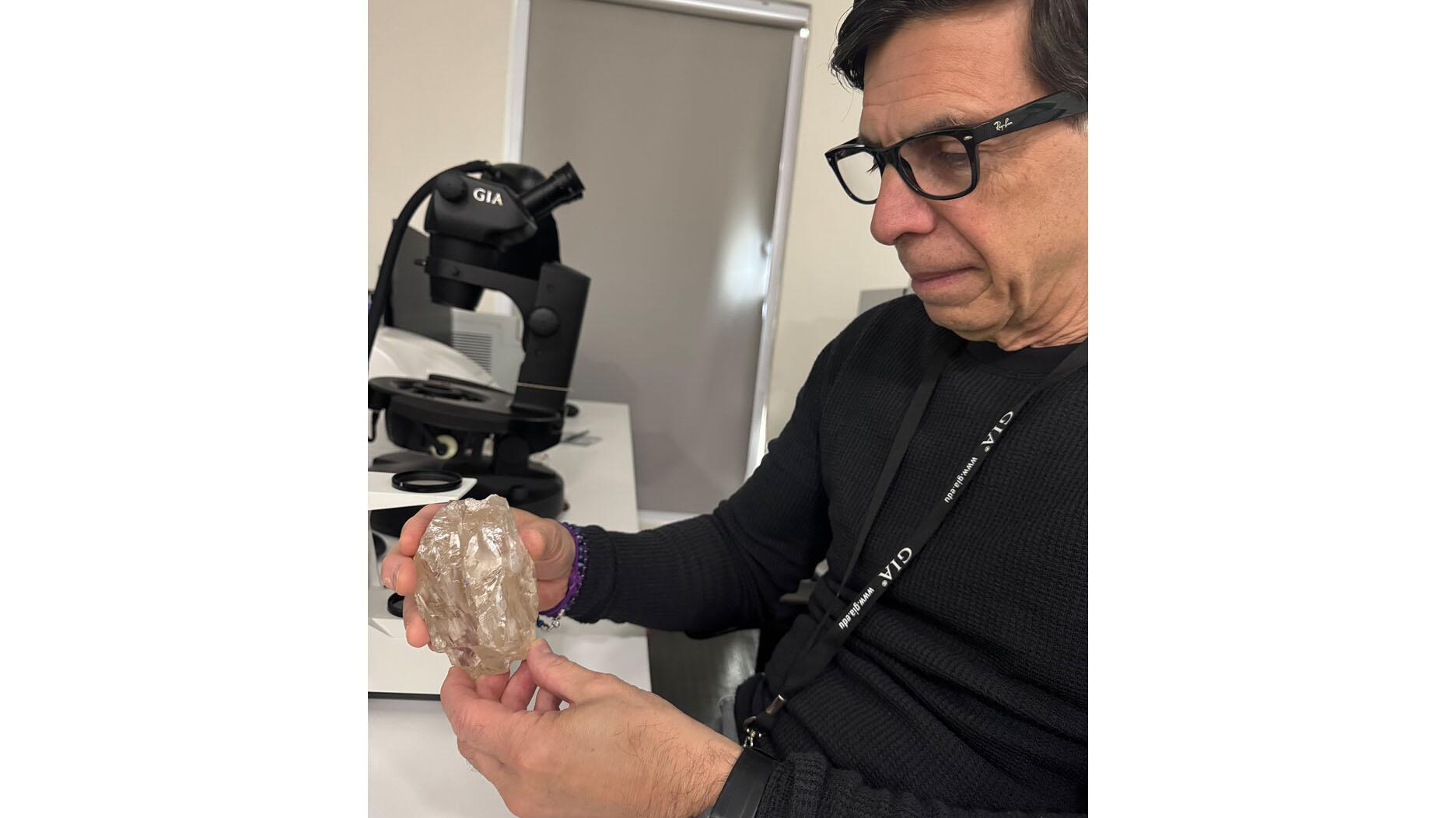
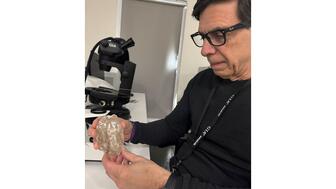
The largest white diamond to come to market in the U.K. in more than a decade, the VVS1, I-color stone is expected to top $1 million.
The ongoing debate over old cuts
The GIA’s new circular brilliant description was created to allay cut grade concerns among antique and estate diamond dealers. But it isn’t enough, some dealers say.

New York--In October, the Gemological Institute of America added a new grading report description for round 58-facet brilliant cut diamonds--the “circular brilliant” cut.
The new category doesn’t take into account table size, as the old European cut designation does. It judges diamonds, instead, on their lower half length (less than or equal to 60 percent, greater than old European cuts) and star facets while also allowing for medium or larger culets.
In addition, like old European cuts, diamonds deemed circular brilliant do not receive a cut grade, as the lab recognizes they were not cut to the same standards as the round brilliants of today.
The new description came about as the result of complaints from antique and estate diamond dealers whose stones don’t quite make the grade as old European cuts--their table is slightly too big or their culet a little too small--and were falling into the round brilliant category, where they sometimes received “fair” or “poor” cut grades.
The issue is of so much concern to those who deal in older diamonds that it was the topic of the educational seminar at the trade-only antiques show last year in Las Vegas.
“We were basically trying to respond to the trade,” said Russell Shor, an industry veteran who’s currently a senior industry analyst with the GIA. “They made a good point. These diamonds are supposed to be cut to 70-, 80-, 90-year-old standards, not current standards. Why should we penalize those goods for no reason? That was what the trade was asking us and we agreed.”
But some who deal in antique diamonds say the addition of the circular brilliant cut description this past fall did little or nothing to rectify the overarching problem, which is this: It’s very difficult, if not impossible, to apply modern science to diamonds that were cut decades ago in disparate factories around the world, without the tools or globally accepted standards that guide the practice today.
They are calling upon the GIA to expand the parameters of what constitutes an old European cut, or, as one dealer suggested, allow those who deal in older stones to opt out of receiving a cut grade entirely.
“It’s just confused the market and they’ve done nothing to rectify (the problem),” antique diamond dealer Michael Goldstein, of Michael Goldstein Ltd., says of circular brilliant. “It’s just too narrow.”
The history behind old cuts
In order to understand the challenges inherent in grading older diamonds today, one first has to know a bit about the history of diamond cutting, and how the industry moved from the old mine and old European cuts through a transitional phase to arrive at the round brilliants of today.
Prior to the patenting of the first, steam-driven bruting machine in 1874, diamond cutters simply took an octahedron--the most common shape for gem diamonds which consists of two four-sided pyramids attached base-to-base--and manually rounded off the corners to create a cushion-shaped stone. They then faceted the diamond from what was left, creating what today is known as an old mine cut.
As a result, they had small tables, steeper crown angles, generally larger culets and short star facets, as well as shorter lower girdle facets, which caused the pavilion main facets to be wide and dominate. (Graduate gemologist and antique diamond dealer Doug Liebman notes that are there are some exceptions to the large culet standard, as some diamonds cut in Antwerp and Amsterdam in the early 1900s did not have culets.)
Over time, however, the world changed, and diamond cutting evolved with it.
The invention of the bruting machine allowed diamond cutters to make round stones instead of just cushion-shaped diamonds, leading to the advent of what today is known as an old European cut.
These stones had the same characteristics as the old mine cut diamonds--small tables, steeper crown angles, short star facets, generally large culets and pavilions characterized by short lower girdle facets and fat pavilion main facets--but were circular in shape.
Sometime after old European cuts came into play, incandescent lighting became more popular for use in home and businesses around the world, changing how people saw many things, including diamonds.
This prompted diamond cutters, beginning in the 1920s, to start lengthening the lower girdle facets, which gave the stones more “life,” or scintillation, under electric light, Yantzer says.
The diamonds cut during this period, from about the 1920s through the 1940s, are often referred to in the trade as “transitional cut” rounds, meaning they were crafted in that era in which the industry was moving from the old mine and old European cuts to the modern round brilliant.
It was these stones the GIA wanted to address in creating the circular brilliant cut. “They were trying to close the gap and I think it was a credible effort,” Liebman says. “The people that work on this were highly knowledgeable.”
In his eyes, though, more needs to be done, both with the parameters for circular brilliant cut and old European cuts, which are too narrow, he says.
Modern-day issues
Some of Liebman’s concerns with the circular brilliant description, it seems, already are being addressed.
He told National Jeweler on Tuesday that he had a positive phone conversation with John King, the GIA’s chief quality officer, Monday about tweaking the lower half length criteria for circular brilliants, increasing it from 60 percent to 65 percent. This would help the category to encompass more stones, Liebman says.
The next phase of his old-cut-clarification mission, he says, is to get the GIA to accept his expanded criteria for old European cuts, which were well received by King during their conversation.
As it stands now, diamonds at the GIA labs must meet three out of the four following criteria to qualify as an old European cut:
Table size: Less than or equal to 53 percent
Crown angle: Greater than or equal to 40 degrees
Lower half length: Less than or equal to 60 percent
Culet size: Slightly large or larger
Liebman says he would like to see the lab expand the table size, increase the lower half length, allow diamonds with a small or larger culet to be accepted, utilize the circular brilliant criteria for star facet length (less than or equal to 50 percent) and add a bruted girdle (a knife-edge girdle that is thin or extremely thin), and include fair or poor symmetry as new criteria. Four or five of these eight criteria should be enough for a diamond to qualify as an old European cut, he says.
He has another solution as well: allow the submitter of a stone to determine whether they want to receive a cut grade.
He says when he submits a diamond to the GIA, he wants the lab to establish the color and clarity and measure them. He doesn’t need a cut grade; he said the market should be allowed to judge the quality of the cut by the value it assigns to the stone.
Goldstein doesn’t want, for example, a diamond from a 1920s Cartier piece coming back as a modern round brilliant with a fair or poor cut grade. It only creates confusion on the back end for him.
“Then customers aren’t happy,” he says. “’They say, ‘Michael, we wanted an old stone. This isn’t old.’”
For the GIA’s part, it is open to future changes to the old European cut description. Shor says the fact that they created the circular brilliant cut in the first place is evidence of the fact that they heed complaints from the industry.
“Everything is a learning process. Of course we wouldn’t rule out any further modifications,” he says.
But, the lab is a scientific organization that issues grading reports--not certificates--and needs to back up any changes with research, just as they did when they first instituted the cut grade in 2006.
“Obviously, we don’t know everything,” Shor says. “If they can make a case, that’s fine.”
Not romanticizing the stone?
Another issue raised by antique diamond dealers is in the name circular brilliant, which does nothing to speak to the historical nature of these stones. As Goldstein, put it: “There’s nothing in history that was called a circular brilliant cut.”
Speaking just as a diamond dealer and not for the committee, Shatz says he is fine with the criteria established for the circular brilliant cut, and he does not agree with the idea of expanding the criteria for old European cuts.
“If you expand that, how far do you expand it? Where do you stop?” he asks. “No matter where you expand the criteria, there are always going to be stones that come close but don’t conform. These changes might include another 10 percent of stones, so what do you do about the stones that fall outside of that?”
Shatz, however, has the same opinion as Goldstein about the name “circular brilliant.” He says he would have preferred calling them “antique style” or something similar that would romanticize these stones a bit more. This would be better than trying to sell a circular brilliant, which is “very generic, at best,” he says.
But Shor says the circular brilliant description was created for all diamonds that don’t conform to the proportions of the modern round brilliant, not just older diamonds.
The category could include stones manufactured relatively recently, including diamonds cut in the 1970s and 1980s when more focus was being placed on weight than cut.
“’Antique style’ implies that they were cut long before that,” he notes.
He adds that antique style also offers no description of diamond shape, which is essential when describing cut.
While the opinions and suggestions on the topic of grading old cut diamonds are many, there is one point upon which it seems everyone would agree: The relatively new debate over these old cut stones is far from over. It is a very complex problem that impacts many diamond dealers and encompasses decades and decades of stones.
There are no easy solutions, and it seems unlikely that the addition of one grading report description, circular brilliant, to going to put an end to the debate.
“It’s hard to put something together and say, ‘that’s it.’ I think they may have to look at it again as time goes on,” Shatz says. “Maybe they will have to change some of the criteria for this new category, and maybe somebody will come up with a better name than calling it circular brilliant.”
The Latest

Skelly shares her plans for reimagining the fine jewelry retailer she re-acquired after it faltered last year.

The collection takes inspiration from the emotional space between people, moments, and experiences.

Every jeweler faces the same challenge: helping customers protect what they love. Here’s the solution designed for today’s jewelry business.

In 2026, the jewelry retailer is celebrating a milestone only a small percentage of family-owned businesses survive to see.


The group of jewelers held a jewelry raffle in support of the Children’s Hospital of Richmond at VCU.

The jewelry giant released preliminary results for the fourth quarter and full year on Monday, with final results slated to come next week.
With refreshed branding, a new website, updated courses, and a pathway for growth, DCA is dedicated to supporting retail staff development.

The retailer also gave an update on its vendor partnerships.

The award-winning actress is the “epitome of modern allure,” the brand said.

The “Bloom” collection draws from the flower power movement of the 1960s and ‘70s with inlay pendants offered in eight colorways.

The unique piece was one of the custom works offered at the foundation's recent silent art auction, which garnered nearly $15,000 in total.

Bulgari named Gyllenhaal as its brand ambassador for his embodiment of artistic depth, intellectual curiosity, and warmth.

Awards were given to four students, one apprentice, and an emerging jeweler.

The top jewelry lot of the late model’s estate sale, hosted by John Moran Auctioneers, was an Oscar Heyman & Brothers for Cartier necklace.

Increased competition, falling lab-grown diamond and moissanite prices, and the rising cost of gold took a toll on the moissanite maker.

The earrings, our Piece of the Week, feature pink tourmalines as planets orbiting around an aquamarine center set in 18-karat rose gold.

“The Price of Freedom” campaign video for International Women’s Day confronts the quiet violence of financial control.

Also, a federal judge has ordered that companies that paid tariffs implemented under the IEEPA are entitled to refunds.

The ever-growing collection, which just expanded with the addition of Olga of Kyiv, features cameos of 12 women from history.

We asked a jewelry historian, designer, bridal director, and wedding expert what’s trending in engagement rings. Here’s what they said.

The annual event will be held in Orlando, Florida, from Sept. 14-17.

The “Outlander” star modeled for the digital cover of the magazine’s spring issue, which features a story on her relationship with jewelry.

This year’s annual congress, which will mark the confederation’s 100th anniversary, will take place this fall in Italy.

Beverly Hills was chosen as the location for the brand’s first store, designed as a “private residence for modern monarchs.”

Kering, Apple, and other retailers have reportedly temporarily closed stores in the Middle East region in light of the recent conflicts.

Beth Gerstein discusses the vibe of the new store, what customers want when fine jewelry shopping today, and the details of “Date Night.”