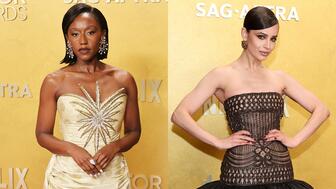Our Pieces of the Week honor the 2026 nominees for the Gem Award for Jewelry Design, Silvia Furmanovich, Cece Fein-Hughes, and Catherine Sarr.
Live from Conclave: Understanding Cybersecurity Risks
Do your employees understand when an email should raise alarm bells? And are you patching your software when prompted?
But that doesn’t mean a small business, like a family-owned jewelry store, can’t be hacked.
“Every organization is a target,” Mary Myers, an information security analyst with Jewelers Mutual Insurance Group, said. “There are just different rationales for why.”
Myers presented a breakout session Monday morning at Conclave outlining the cybersecurity risks businesses face and detailing what jewelers should do if they are hacked.
She started with social engineering and phishing.
Social engineering is the act of manipulating employees into doing something they otherwise would not do. Phishing is social engineering via email and can involve attachments, directing the recipient to fake websites, or fake emails.
Myers said phishing emails are often unexpected and written in a way that makes them seem urgent (your immediate reply is requested, etc.).
While they can contain misspellings and grammatical errors, she noted that hackers are getting smarter and cleaning up their emails so there are fewer of these. Phishing messages also can come from email addresses that are nearly identical to (or exactly the same as, which is called spoofing) those of people with whom the business owner and/or employees communicate regularly.
The emails try to bait the the receiver into replying and engaging in a conversation, opening an attachment or clicking a link for the purposes of installing malware on the business’ computer systems.
The malware widely in use by hackers right now is called ransomware, Myers said. Hackers lock victims’ computers with encryption and demand they pay a ransom, via Bitcoin, to get their data back.
Her initial recommendation is, of course, not to click on links or open the attachments in emails that seem suspicious. Delete the email, call the sender and ask if they sent that specific email with an attachment or consult IT support.
But that doesn’t always happen.
When a business owner or employee falls for a phish, Myers said options are somewhat limited.
She said what business owners should not do is pay, as there is no guarantee they will get their data back.
Jewelers also face cybersecurity risks from both employees and vendors/contractors who could accidentally load a virus onto a system by clicking a phishing link or visiting a disreputable site, or who could violate a business intentionally, by purposely loading or sending a virus or sharing sensitive customer information. Myers said business owners need to provide guidance to employees, vendors and contractors and to clearly define: what does acceptable internet use at the company look like?
While not heavily attended, the Conclave session did generate multiple questions from attendees.
One jeweler asked if should she turn off her servers at night to help protect against attacks. You can, Myers answered, but it won’t necessarily prevent anything, as some of this software is malware designed to enter the system and lie dormant until it can be activated.
Another asked if paid-for anti-virus software is better than free. Myers said anything that will help a business quarantine and clean up a virus is “great.” What will work best a particular business really depends on its size, needs and risk factors.
Myers wrapped up with a list of a half-dozen additional tips for increasing cybersecurity.
1. Keep an inventory of key systems and applications.
2. Keep an inventory of risks and threats, and use multiple layers of security.
3. Keep systems and devices patched.
All software has “gaps” that make it vulnerable to hackers, Myers said. “Patches” are released regularly by software companies and are intended to seal those gaps. Microsoft releases patches for its software on a monthly basis, but probably the most well-known example of a patch are the “updates” Apple regularly sends for iPhones and iPads.
“If you don’t close it,” Myers said of the gap, “you’re exposed. Patching is super, super critical.”
4. Back up systems and, Myers added, test the back-up.
Having a virus-infected system is going to create an “emotionally charged” situation. She said business owners don’t want that to be the first time they’ve ever walked through the process of employing their back-up.
5. Establish separation in key systems.
Business owners who host their own websites should separate it internally and not have it on the same server as the rest of their data. They also need to rotate job duties. They can’t “give the keys to the kingdom” to one person; hackers would have to have access to several people if there's separation.
Also, when someone leaves the company, take away their access to the company’s systems.
6. Train employees on cyber risks at least annually, if not quarterly.
In response to one jeweler’s question, Myers said business owners can require employees who connect personal devices to the store’s Wi-Fi to update those devices when prompted. She recommended writing it into the store’s policy.
The JSA also recently released a list of cybersecurity recommends, which was included in National Jeweler’s article about Saks getting hacked.
The Latest

The 24-piece watch collection is set to debut in spring 2027.

Pooler, who has more than 25 years’ experience in jewelry, is now chief operating officer of Modani Jewels, Soham Diamonds, and SNJ Creations.

Every jeweler faces the same challenge: helping customers protect what they love. Here’s the solution designed for today’s jewelry business.

The reopening of the Waldorf Astoria means a homecoming for the industry group’s annual event, which will take place Saturday.


McCormack looked to the 19th century’s “golden age” of astronomy when designing her new celestial-themed collection.

The new smart design software allows jewelers to configure, price, and confirm a custom engagement ring in real time for in-store customers.
With refreshed branding, a new website, updated courses, and a pathway for growth, DCA is dedicated to supporting retail staff development.

The 10,000-square-foot diamond manufacturing facility officially opened in late February and employs 50 people.

The largest white diamond to come to market in the U.K. in more than a decade, the VVS1, I-color stone is expected to top $1 million.

Skelly shares her plans for reimagining the fine jewelry retailer she re-acquired after it faltered last year.

The collection takes inspiration from the emotional space between people, moments, and experiences.

In 2026, the jewelry retailer is celebrating a milestone only a small percentage of family-owned businesses survive to see.

The group of jewelers held a jewelry raffle in support of the Children’s Hospital of Richmond at VCU.

The jewelry giant released preliminary results for the fourth quarter and full year on Monday, with final results slated to come next week.

The retailer also gave an update on its vendor partnerships.

The award-winning actress is the “epitome of modern allure,” the brand said.

The “Bloom” collection draws from the flower power movement of the 1960s and ‘70s with inlay pendants offered in eight colorways.

The unique piece was one of the custom works offered at the foundation's recent silent art auction, which garnered nearly $15,000 in total.

Bulgari named Gyllenhaal as its brand ambassador for his embodiment of artistic depth, intellectual curiosity, and warmth.

Awards were given to four students, one apprentice, and an emerging jeweler.

The top jewelry lot of the late model’s estate sale, hosted by John Moran Auctioneers, was an Oscar Heyman & Brothers for Cartier necklace.
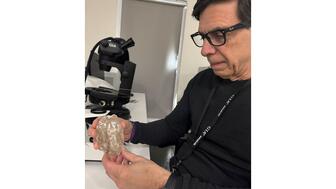
Moses, who started at GIA’s Santa Monica lab in 1976, will leave the Gemological Institute of America in May.

Increased competition, falling lab-grown diamond and moissanite prices, and the rising cost of gold took a toll on the moissanite maker.

The earrings, our Piece of the Week, feature pink tourmalines as planets orbiting around an aquamarine center set in 18-karat rose gold.

“The Price of Freedom” campaign video for International Women’s Day confronts the quiet violence of financial control.

Also, a federal judge has ordered that companies that paid tariffs implemented under the IEEPA are entitled to refunds.