Set in a Tiffany & Co. necklace, it sold for $4.2 million, the highest price and price per carat paid for a Paraíba tourmaline at auction.
What Tiffany’s Acquisition Means for the Jewelry Industry
Looking at what makes Tiffany & Co. worth $16 billion says a lot about what consumers value, Associate Editor Lenore Fedow writes in her analysis of the deal.

Life as the resident retail reporter at National Jeweler can be a bit of a bummer.
It’s an unofficial and self-bestowed title, but if stores are closing or companies are going bankrupt, I tend to cover it.
Truly, I like my beat. I do my best work when I’m elbow-deep in quarterly reports and court documents.
But when the rumors of LVMH’s acquisition of Tiffany & Co. began to fly, I felt a bit uneasy.
As a lifelong New Yorker, I have a soft spot for Tiffany. My everyday jewelry, the pieces I consider a part of me, all came in a little blue box.
I see the company as an American icon and quintessentially New York, and I wasn’t sure how to feel about a French luxury conglomerate buying it.
As a reporter covering retail, I mulled over what the deal would mean for Tiffany and, more broadly, for the jewelry industry at large.
So I picked the brains of experts and analysts, and I’ve come to you with my findings.
Here’s what makes Tiffany so valuable and why those factors matter to the overall industry.
Tiffany brings a strong brand to the table.
Amid reports of a potential acquisition, Tiffany confirmed in October it had received an unsolicited bid from LVMH for $120 per share, valuing the company at $14.5 billion.
After talks with LVMH, Tiffany reportedly asked the company to up the bid to $130, believing the company was worth more.
And Tiffany was right. The final deal was for $135 per share, or $16.2 billion, one of the largest transactions in LVMH’s history.
Tiffany was able to command big bucks, in part, because of the strength of its brand.
Flavio Cereda, an equity analyst at Jeffries, stated in a note written prior to the deal that Tiffany’s “brand equity and the strength of the image of its iconic 1837 Blue Box are more valuable than the current financials suggest.”
“LVMH, with all its brands, does not have a strong, solid diamond jewelry brand like Tiffany or that caters to Tiffany’s clientele,” industry analyst Edahn Golan wrote in an email to National Jeweler.
LVMH’s watch and jewelry portfolio consists of Chaumet, Bulgari, Fred, Hublot, TAG Heuer, and Zenith.
“Of the six companies in LVMH’s watch & jewelry group, only Chaumet is a diamond jewelry company, which means that the group has a lot of room to grow,” he said.
From its trademark Tiffany Blue color to the white ribbon around its
The rise of brands was a major takeaway from De Beers’ 2019 Diamond Insight Report, which noted the popularity of branded jewelry, particularly in the diamond engagement ring space.
Branded jewelry represents two-fifths of sales of commitment jewelry in the United States, said De Beers.
The report also highlighted the resonance of brands with same-sex couples and millennials.
Tiffany’s vertical integration is valuable.
“Tiffany checked all the boxes,” industry analyst Paul Zimnisky said in an interview with National Jeweler Friday, noting that while the standalone brand was the most important aspect of the deal, its vertical integration is certainly the second.
Luca Soltani, senior research analyst for luxury goods at research firm Bernstein, echoed Zimnisky’s sentiment on vertical integration.
“It is clearly an advantage—especially when we look at the bridal products,” Soltani said in an email to National Jeweler.
Zimnisky wasn’t surprised by the acquisition, as rumors had been swirling in the space for a while, but said he was surprised LVMH didn’t make a bid last year during the stock market sell-off.
Then again, “not a lot of acquisitions could move the needle for them,” he said, noting the size and wealth of the luxury conglomerate.
LVMH has the money to spend, but what it lacks are the sourcing and manufacturing connections that Tiffany maintains.
LVMH Chief Financial Officer Jean-Jacques Guiony said as much in a conference call with analysts following the deal, highlighting Tiffany’s “very high level of vertical integration, compared with our brands.”
“[Tiffany] realized early on that vertical integration will give it better access to the goods it needs, and at better prices too,” said analyst Golan.
The company’s vertical integration efforts began 20 years ago, Tiffany CEO Alessandro Bogliolo said in an interview with Bloomberg.
Tiffany established Laurelton Diamonds, a wholly owned manufacturing subsidiary, in 2002.
It’s a De Beers sightholder and has inked long-term rough supply agreements with Alrosa and Dominion Diamond.
Bogliolo noted that 80 to 90 percent of its polished diamonds above 0.18 carats come from its workshops.
Tiffany also holds a stake in a diamond mine in South Africa owned by Canadian mining company Diamcor, a company spokesperson confirmed.
At a time when provenance and supply chain transparency are becoming increasingly important to consumers, Tiffany is ahead of the curve.
The jeweler began telling consumers the origin of its diamonds in January through its “Diamond Source Initiative.”
In that same Bloomberg interview, Bogliolo estimated the move toward sustainability cost Tiffany tens of millions of dollars over the years but added that it differentiates Tiffany from other jewelry companies.
“The reason why we are so selective with our sourcing is to avoid either mines that are not compliant with safety requirements, environmental protection, [and] human rights respect,” he said.
Tiffany, for example, does not source from Zimbabwe or the Congo due to internal issues in the countries, even if the diamonds meet Kimberley Process standards, he said.
“Tiffany is a very big player in all sorts of diamonds, and it’s something where the sourcing is not easy to do, and we expect to benefit from that,” LVMH’s Guiroy said on the call.
Tiffany boarded the sustainability train early.
With Tiffany’s vertical integration comes its ability to have a greater say in the means of production, a valuable asset at a time when climate change and environmental issues are weighing heavy on the minds of many consumers.
The younger, affluent generation are socially and environmentally conscious and hold luxury brands to high standards, particularly sustainable and ethical production processes, said Deloitte in its Global Powers of Luxury Goods 2019 survey.
In addition to its diamond sourcing standards, the jeweler has been mindful of metals.
A decade ago, Tiffany was the first jewelry company to speak out against the development of the never-built Pebble Mine in Alaska’s Bristol Bay, holding a screening of a documentary about the importance of the watershed, “Red Gold,” in New York.
It was one of the first jewelers to use gold sourced from the “Salmon Gold” initiative, which aims to mine gold in a way that’s mindful of the habits of salmon and other fish.
The Deloitte study highlights Tiffany’s responsible sourcing as well as its social and environmental work, particularly its philanthropic foundations focusing on reef conservation and awareness for responsible mining.
Tiffany created its “Save the Wild” collection in 2017, donating all profits, totaling more than $5 million, to the Wildlife Conservation Network.
And the company’s over-the-top holiday catalog offers an 11-day safari in Kenya and a set of animal-shaped diamond brooches, with a portion of the proceeds going to the animal conservation charity.
Tiffany is doing well in a key market—China.
Luxury brands across the board are grappling with U.S.-China trade tensions. Simultaneously, political unrest in Hong Kong is weighing heavy on balance sheets.
Tiffany, however, is still seeing double-digit growth in mainland China and highlighted higher spending by locals in its third-quarter results.
The jeweler currently has 35 stores in mainland China and 10 in Hong Kong.
LVMH’s third-quarter results also reported strong growth in Asia, and it has a strong enough foothold in the country to propel Tiffany even further in the growing market.
Jefferies analyst Cereda said LVMH may leverage the strength of Tiffany’s brand to target the Asian millennial market.
“I could definitely see that happening,” said Reginald Brack, executive director at NPD and an industry analyst on watches and luxury, in an interview with National Jeweler Friday.
“I think that Asian millennial luxury consumer is what most luxury brands now are trying to target. Tiffany is well-poised and positioned to capitalize on that with their immense brand recognition.”
The future of Tiffany may mean fewer stores.
Cereda noted Tiffany’s move into China may mean a “rethinking of the current product mix and its U.S. footprint.”
Bernstein analyst Soltani said Tiffany’s position in the United States is a strength, but that perhaps, “LVMH would want to upgrade the Tiffany flagship stores, and streamline the rest of the retail network.”
Tiffany’s flagship New York City store will undergo renovations after the holiday, and the retailer will move the store into a temporary, nearby space until it’s completed.
He said in secondary locations, Tiffany could “use a lighter (and smaller) retail format.”
NPD analyst Brack had the opportunity to visit a new Tiffany concept store in Tokyo, which he described as an “industrial loft space” that included a permanent DJ booth.
He said the items were more accessible, out there in the open to touch, and the space had a personalization bar.
An openness to change in an ever-changing retail environment is critical and when you have a strong brand, you can afford to experiment a little.
This deal speaks to the industry at large.
What I’ve taken away from my discussion with experts and analysts is this: Looking at what makes Tiffany worth $16 billion says a lot about what consumers value.
To compare Tiffany with independent jewelers is incongruous in some respects but, overall, understanding what matters to the customer is vital to any business.
Tiffany has: a strong brand, control of aspects of production, a focus on responsible sourcing and sustainability, and an eye for the retail experience.
Whether upping your social media game or talking more with your customers about the journey their jewelry has taken, you can take away something actionable from this historic deal.
The Latest

The jeweler’s “Deep Freeze” display showcases its iconic jewelry designs frozen in a vintage icebox.

Take luxury gifting to new heights this holiday season with the jeweler’s showstopping 12-carat sphene ring.

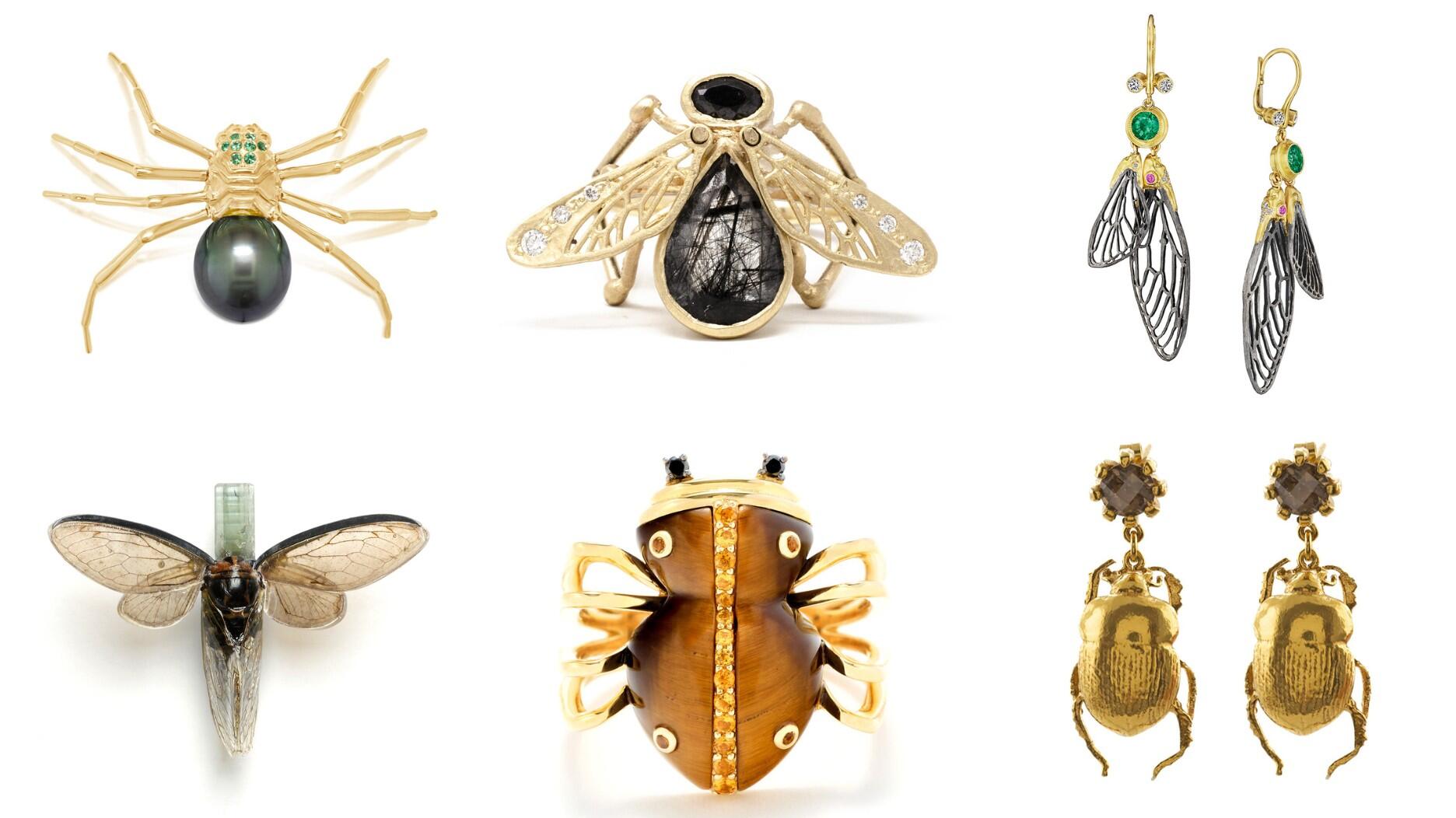
How Jewelers of America’s 20 Under 40 are leading to ensure a brighter future for the jewelry industry.

This year's theme is “Unveiling the Depths of the Ocean.”


In its annual report, Pinterest noted an increase in searches for brooches, heirloom jewelry, and ‘80s luxury.

Starting Jan. 1, customers can request the service for opal, peridot, and demantoid garnet.

Roseco’s 704-page catalog showcases new lab-grown diamonds, findings, tools & more—available in print or interactive digital editions.

The 111-year-old retailer celebrated the opening of its new location in Salem, New Hampshire, which is its third store in the state.

The new catalog features its most popular chains as well as new styles.

The filmmaker’s personal F.P. Journe “FFC” prototype was the star of Phillips’ recent record-setting watch auction in New York.

The new location in the Design District pays homage to Miami’s Art Deco heritage and its connection to the ocean.

Inflations, tariffs, and politics—including the government shutdown—were among consumers’ top concerns last month.

“Longtime favorite” presenters, as well as first-time speakers, will lead talks and workshops at the annual event in Tucson next year.

Silas Smith of Meridian Metalworks won the challenge with his pendant that blends Australian and American landscapes.

The sale of the 31.68-carat, sunset-hued stone was part of Sotheby’s first series of events and auctions in Abu Dhabi.

Most customers who walk into your store this month have made up their minds. Your job is to validate their choice, Emmanuel Raheb writes.

The collection features characters and motifs from Ukrainian folklore, including an enchanted mirror and a magic egg.

MatrixGold 3.11, the newest version of the jewelry design program, offers more flexibility, precision, and creative control.

The pavilion will be part of the 2026 JA New York Spring show, scheduled for March 15 to 17.

Kadet, a 1994 National Jeweler Retailer Hall of Fame inductee, helped grow the family-owned retailer in the Chicago area and beyond.

Billed as the world’s smallest wearable, Lumia Health’s new smart earrings have a health tracker subtly embedded in the back.

Don’t let those with December birthdays feel blue. Help them celebrate their month with blue zircon, turquoise, and tanzanite.
The new pink sapphire version of the piece dances with its wearer in the brand’s “Icons After Dark” holiday campaign.

A choice that’s generated a lot of commentary, Pantone says “Cloud Dancer” marks a fresh start and encourages relaxation and creativity.

The manufacturer’s holiday campaign features a gift guide filled with trending designs and jewelry that can be personalized.

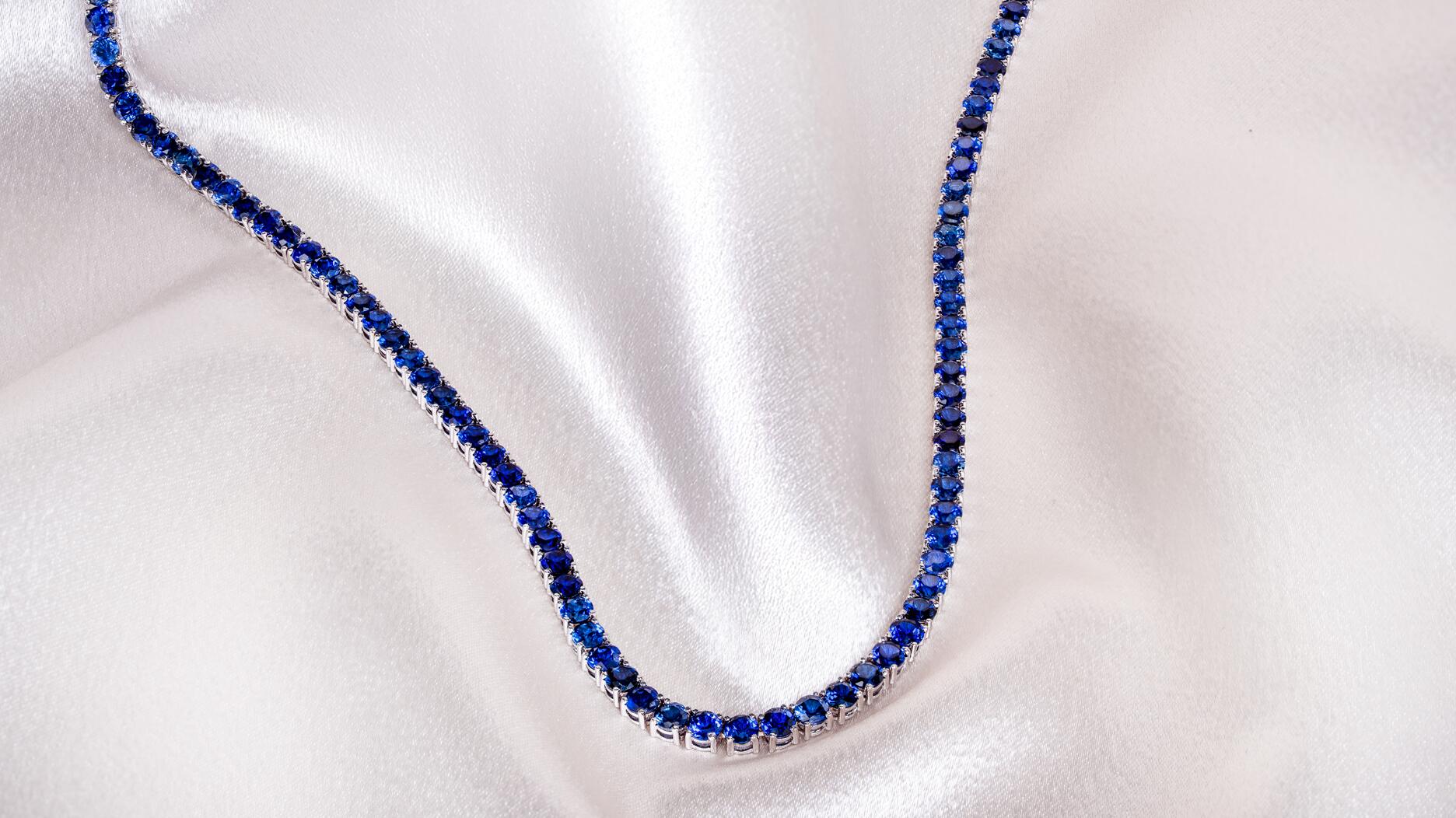
The man was charged with theft, accused of ingesting the necklace while in a jewelry store in Auckland, New Zealand.


























