5 Interesting Facts You Might Not Know About Diamonds
Editor-in-Chief Michelle Graff recaps a webinar in which she learned more about the stones’ formation, inclusions and the oldest diamonds on Earth.

I had a great deal of fun doing it, and it served as a much-needed reminder of how much I like to just write, not necessarily about a controversy or a lawsuit, or with clicks in mind, but just for the sheer pleasure of finding an expressive way of sharing something I enjoy.
With that in mind, I’m having fun again this week, this time by sharing five facts about diamonds gleaned from a webinar.
On Thursday, geologist Evan Smith, a research scientist at the Gemological Institute of America, held the first in what is going to be a series of online “Knowledge Sessions” presented by GIA.
The webinars will feature presentations on gemology from scientists, field gemologists and educators, continuing next Thursday with Mike Breeding, GIA senior research scientist, talking about identification methods for lab-grown diamonds.
(GIA is currently building a web page for its Knowledge Sessions; we will share it as soon as it is available.)
Smith’s talk, “The Unique Story of Natural Diamond,” focused on what makes the hardest substance on Earth—and one of the world’s most popular gemstones—so interesting to geologists.
I’ve interviewed and written about Smith’s research here and there over the years; he was the lead author of an article on blue diamonds that landed on the cover of Nature, a scientific journal, in 2018, and his diamond research made the cover of Science in 2016.
He alluded to both these studies in his presentation and taught me a few new things about diamonds as well.
Please feel free to comment below if you’ve learned anything, or if you just feel like saying hello. You also can view the presentation in its entirety on YouTube.
1. Diamonds form deeper in the earth than other minerals.
Most minerals including corundum (ruby and sapphire) and beryl (emerald, aquamarine and morganite) form in the Earth’s crust, which is the layer upon which we all live.
But not diamond, which Smith said is “completely exotic … because it is formed much deeper in the Earth,” beneath the crust at depths of 150-200 kilometers (93-124 miles) in the base of old, thick continents.
Some go even deeper than that, forming at the boundary between the Earth’s mantle and its outer core. These are known as superdeep diamonds.
(For those needing a visual refresher on the layers of the Earth, I found this diagram to be helpful.)
Smith said “very energetic” volcanic eruptions that come from below 200 kilometers bring diamonds to the surface. They are a sort of “accidental passenger” in these explosions.
With them, they carry valuable information in their mineral inclusions, which most commonly include kyanite, garnet and olivine.
Diamond inclusions can help researchers understand the distribution of elements in the Earth’s layers, for example, or when plate tectonics started.
“The diamond is surprisingly good at preserving these materials,” Smith said. “It’s very hard and durable, and good at keeping things from diffusing, or leaking, out of it, and diffusing, or leaking, into it.
“There’s a tremendous of information trapped in these diamonds.”
2. Superdeep diamonds were completely misunderstood until a few years ago.
For many years, diamonds that form at depths greater than 200 kilometers were believed to be small and never gem quality.
But in the past four years, Smith said, researchers have found that many large, high-quality diamonds—Type IIa diamonds (stones with top color and clarity) and Type IIb diamonds, which are gray or blue because of the presence of boron—are actually superdeep stones.
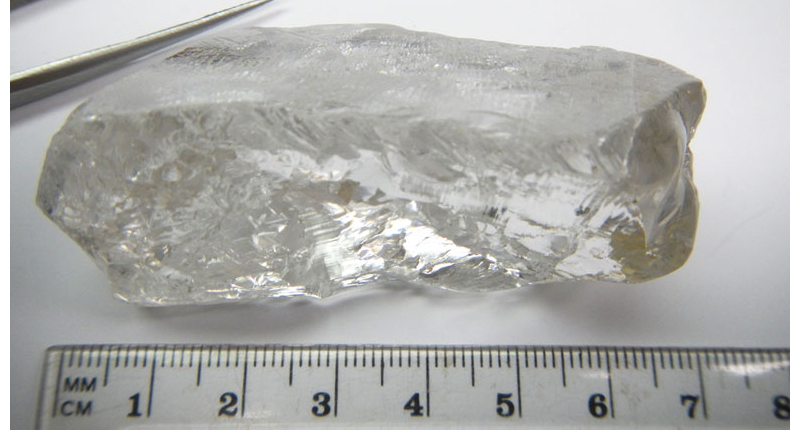

One example of a superdeep diamond is the 404-carat rough diamond recovered from the Lulo Mine in Angola in 2016 (pictured above). Immediately found to be Type IIa and D color, it was the biggest diamond ever known to come from Angola.
The 813-carat Constellation diamond from the Karowe mine in Botswana also is a superdeep diamond, as is the famous Hope diamond and, of course, the largest diamond ever found, the 3,106-carat Cullinan.
Smith said superdeep diamonds are identifiable by the presence of high-pressure mineral inclusions like Ca-pv, calcium perovskite.
3. There are more diamond types than you might think.
Generally, when we talk about diamond types in the trade, we think of Type IIa or Type IIb, terms that speak to a diamond’s physical appearance, its color and clarity and, thereby, its value.
But to geologists like Smith, there are also eclogitic and peridotitic diamonds, two terms I had never heard prior to Thursday’s lecture.
Peridotite and eclogite are two types of rock found in the Earth’s mantle, and diamonds can form in both. These are not superdeep diamonds but the ones found closer, relatively speaking, to the surface of the Earth, also known as lithospheric diamonds.
Peridotite is an igneous rock and is the predominant rock type found in the mantle. If researchers find olivine inclusions in a diamond, then it tells them the host rock was peridotite.
A metamorphic rock, eclogite is much less common. The presence of kyanite inclusions in a diamond indicates it formed in eclogite rock.

4. The oldest diamonds in the world are found in Canada.
Smith’s presentation included a timeline (who doesn’t love a timeline?) that illustrated just how old diamonds are relative to the history of, well, everything.
The Earth dates back 4.5 billion years while the planet’s oldest rocks, found in Northern Quebec, are 4.3 billion years old.
The oldest diamonds follow at 3.5 billion years old and, like the Earth’s oldest rocks, come from Canada, a fact I already was aware of after hearing Karen Smit, another GIA research scientist, speak about the GIA’s Diamond Origin Program back in the fall.
Smit said the oldest diamonds studied by geologists so far have come from the Diavik mine, which Rio Tinto owns and operates in partnership with Dominion Diamond Corp.
To put this in perspective: All these diamonds are older than the Atlantic Ocean, which opened up when supercontinent Pangaea began to break apart about 200 million years ago, and the dinosaurs, which died off 65 million years old.
5. Pliny the Elder had something to say about diamonds.
Smith opened up his talk with a quote from Pliny the Elder, a Roman philosopher and naturalist who lived about 2,000 years ago: “Diamond is the most valuable, not only of the precious stones, but of all things in this world.”
And he concluded it with a quote from himself that I liked: “Every diamond tells a story from a place we can’t go and from a time long since passed.”
I’ve now shared a Pliny the Elder quote; my week is complete.
Have a great weekend everyone, and stay safe.
The Latest

Bulgari named Gyllenhaal as its brand ambassador for his embodiment of artistic depth, intellectual curiosity, and warmth.

Awards were given to four students, one apprentice, and an emerging jeweler.

The top jewelry lot of the late model’s estate sale, hosted by John Moran Auctioneers, was an Oscar Heyman & Brothers for Cartier necklace.

Every jeweler faces the same challenge: helping customers protect what they love. Here’s the solution designed for today’s jewelry business.
Moses, who started at GIA’s Santa Monica lab in 1976, will leave the Gemological Institute of America in May.


Increased competition, falling lab-grown diamond and moissanite prices, and the rising cost of gold took a toll on the moissanite maker.

The earrings, our Piece of the Week, feature pink tourmalines as planets orbiting around an aquamarine center set in 18-karat rose gold.
With refreshed branding, a new website, updated courses, and a pathway for growth, DCA is dedicated to supporting retail staff development.

“The Price of Freedom” campaign video for International Women’s Day confronts the quiet violence of financial control.

Also, a federal judge has ordered that companies that paid tariffs implemented under the IEEPA are entitled to refunds.

The ever-growing collection, which just expanded with the addition of Olga of Kyiv, features cameos of 12 women from history.

We asked a jewelry historian, designer, bridal director, and wedding expert what’s trending in engagement rings. Here’s what they said.

The annual event will be held in Orlando, Florida, from Sept. 14-17.

The “Outlander” star modeled for the digital cover of the magazine’s spring issue, which features a story on her relationship with jewelry.

This year’s annual congress, which will mark the confederation’s 100th anniversary, will take place this fall in Italy.

Beverly Hills was chosen as the location for the brand’s first store, designed as a “private residence for modern monarchs.”

Kering, Apple, and other retailers have reportedly temporarily closed stores in the Middle East region in light of the recent conflicts.

Nearly half of buyers are prioritizing silver and fashion collections this season, organizers said.

The “Live Now. Polish Later.” campaign features equestrians wearing the brand’s jewels while galloping across the icy plains of Kazakhstan.

The precious metals provider has promoted Jennifer Ashworth to the role.

Nelson will be honored as the inaugural grant winner at the Gem Awards gala on March 13.

Experts from India weigh in the politics, policies, and market dynamics for diamantaires to monitor in 2026 and beyond.

The American precious metals refiner’s day-to-day operations remain the same post-acquisition.

These aquamarine jewels channel the calming energy of the March birthstone.

The “Innovative Design” category and award will debut in the Spectrum division of this year’s AGTA Spectrum & Cutting Edge Awards.

Consumers were somewhat less worried about the future, though concerns about rising prices and politics remained.

Foerster is this year’s Stanley Schechter Award recipient.