Awards were given to four students, one apprentice, and an emerging jeweler.
The History Behind … Cameos
Jewelers’ love affair with cameos has been recurrent since the Roman era, and a handful of contemporary designers continue to innovate the iconic jewelry style.

New York--Iconic jewelry trends have a way of resurfacing through the centuries, and the cameo is a perfect example.
Experts say that the jewelry style enjoyed the greatest popularity during the Roman era, the Renaissance and the 19th century.

“The cameo, perhaps more than any other form of jewel, has been appreciated as a work of art and an object of virtue since ancient times through to the Renaissance era and the Neo-classical period,” said Michele Rowan, owner of antique store Rowan & Rowan and author of “Nineteenth Century Cameos.”
Today, a handful of designers make the classic style their own, whether as the signature of their brand, like Amedeo Scognamiglio, or as one element of their oeuvre, like Jacquie Aiche, Wilfredo Rosado, Lydia Courteille and Laura Lee.
National Jeweler spoke with Scognamiglio, Rowan, and Emily Stoehrer, the Rita J. Kaplan and Susan B. Kaplan Curator of Jewelry at the Museum of Fine Arts, Boston, on the cameo’s continued reemergence through the ages.
When did cameos first appear in history?
“You really see them in the Roman period,” said Stoehrer. “Then there’s a revival of them in the Renaissance period when there’s this renewed interest in classical art and then you see them go in and out of fashion in the 19th and 20th century.”
According to Stoehrer, cameos passed down through generations were sometimes repurposed, leaving the cameo itself intact but updating the setting for modernity.
This practice is still employed by designers like Aiche, who uses either vintage cameos or carved versions of her own creations, as well as Courteille.
What were they made of?
“Cameos are relief carvings, in effect miniature sculptures,” Rowan explained. “The mediums they were carved from were mainly agate or various types of shell. Gem engravers carved each stone or shell by hand to create figures or scenes, which stood proud from their background.”
“The carver exploits the different variations of color that are in the layers of shell or stone and with that they’re able to carve different motifs in low relief,” said Stoehrer.
What subjects do cameos portray?
No matter the period a cameo was created, the subject matter
“The subject matter rarely varied, most cameos--whether ancient or 17th, 18th or 19th century-- tended to depict scenes or personalities from Greek mythology. The universal appeal of tales of love, loss, deception and magic endured,” said Rowan.

“You’ll typically see allegorical themes, portraits or mythic figures like Medusa for example,” said Stoehrer.
Stoehrer noted that while mythology has been the predominant theme of cameos, some were commissioned to depict real people, a particularly good example of which can be found in bracelet-form in the Museum of Fine Arts, Boston’s permanent collection.
“The bracelet has four cameos representing the Hunt brothers,” she said. “Each one is in the likeness of one of the four brothers and it was donated to the Museum of Fine Arts by their sister.”
Who would typically buy or commission a cameo?
The MFA’s cameo collection features pieces that originated in the collections of the wealthy and influential elite, Stoehrer explained, such as one that belonged to Flemish Baroque artist Peter Paul Rubens.

Rowan explained that, later on, the owning of cameos became more democratic.
“During the 19th century, the cameo moved from the realm of the wealthy cabinet collector to a wider audience,” she said. “Increased wealth among the European middle class and increased travel meant a demand for souvenirs, especially from trips to Italy. The shell cameo industry in Italy increased in size to meet demand.”
What about the cameo’s decline after Victorian times?
In the earliest part of the 20th century, the cameo peaked.
At the time, the image of a woman wearing a choker was an extremely popular figure portrayed in cameos, so popular, said Stoehrer, that it saturated the market and fell out of favor.
As chokers became mass-produced, the quality also suffered.
“The advent of the machine-carved cameo led to a serious decline in quality,” said Rowan.
The Cameo Now
Scognamiglio’s pioneering of the ancient trend has created the cameo’s biggest contemporary success story.
Rare for a modern artist, the Italian-born designer learned to carve cameos in the ancient technique.
“My family has been making cameos since 1857, basically all branches of my paternal family have been either master carvers or cameo manufacturers, throughout two centuries,” said Scognamiglio, who nevertheless, is a self-taught carver, as his family expected his interest in cameos to be a passing fancy.
Scognamiglio started with classic themes found in Greek and Roman mythology, and mastered these before deciding to put his own stamp on the art form.
He created works depicting monkeys, skulls, elephants and crowns, combining ancient craft with rock ‘n’ roll modernity.
He explained, “I made them cool again, contemporary again. And only someone with my long heritage and family tradition, only someone from the bench like me could have done so. I decided I would revolutionize the idea of cameos.”
Scognamiglio opened a boutique in New York City in 2006, eventually expanding to also sell at other retailers. Ten years later, his business is still booming, and he’s known as “the king of cameos.”
“I thought that there was not much interest in cameos now,” said Stoehrer. “I’ve heard from different dealers that they collect dust in their show room, but I had a group in at the MFA who completely disagreed and thought that cameos were really gaining popularity right now. Maybe this is their moment.”
Scognamiglio’s works are particularly popular for their tongue-in-cheek motifs, but the designer couldn’t have created them without studying what came before.
“Evolution comes from a long way,” he said, “from research, study and classical practice.”
The Latest

The top jewelry lot of the late model’s estate sale, hosted by John Moran Auctioneers, was an Oscar Heyman & Brothers for Cartier necklace.
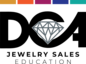
Moses, who started at GIA’s Santa Monica lab in 1976, will leave the Gemological Institute of America in May.

Every jeweler faces the same challenge: helping customers protect what they love. Here’s the solution designed for today’s jewelry business.

Increased competition, falling lab-grown diamond and moissanite prices, and the rising cost of gold took a toll on the moissanite maker.


The earrings, our Piece of the Week, feature pink tourmalines as planets orbiting around an aquamarine center set in 18-karat rose gold.

“The Price of Freedom” campaign video for International Women’s Day confronts the quiet violence of financial control.
With refreshed branding, a new website, updated courses, and a pathway for growth, DCA is dedicated to supporting retail staff development.

Also, a federal judge has ordered that companies that paid tariffs implemented under the IEEPA are entitled to refunds.

The ever-growing collection, which just expanded with the addition of Olga of Kyiv, features cameos of 12 women from history.

The annual event will be held in Orlando, Florida, from Sept. 14-17.

The “Outlander” star modeled for the digital cover of the magazine’s spring issue, which features a story on her relationship with jewelry.

This year’s annual congress, which will mark the confederation’s 100th anniversary, will take place this fall in Italy.

Beverly Hills was chosen as the location for the brand’s first store, designed as a “private residence for modern monarchs.”

Kering, Apple, and other retailers have reportedly temporarily closed stores in the Middle East region in light of the recent conflicts.

Beth Gerstein discusses the vibe of the new store, what customers want when fine jewelry shopping today, and the details of “Date Night.”

Nearly half of buyers are prioritizing silver and fashion collections this season, organizers said.

The “Live Now. Polish Later.” campaign features equestrians wearing the brand’s jewels while galloping across the icy plains of Kazakhstan.

The precious metals provider has promoted Jennifer Ashworth to the role.

Nelson will be honored as the inaugural grant winner at the Gem Awards gala on March 13.

Experts from India weigh in the politics, policies, and market dynamics for diamantaires to monitor in 2026 and beyond.

The American precious metals refiner’s day-to-day operations remain the same post-acquisition.

These aquamarine jewels channel the calming energy of the March birthstone.

The “Innovative Design” category and award will debut in the Spectrum division of this year’s AGTA Spectrum & Cutting Edge Awards.
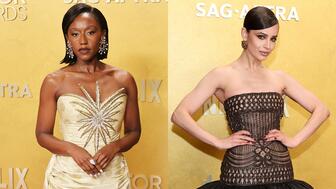
Diamond jewelry was the star of the event formerly known as the SAG Awards.

Consumers were somewhat less worried about the future, though concerns about rising prices and politics remained.

Foerster is this year’s Stanley Schechter Award recipient.