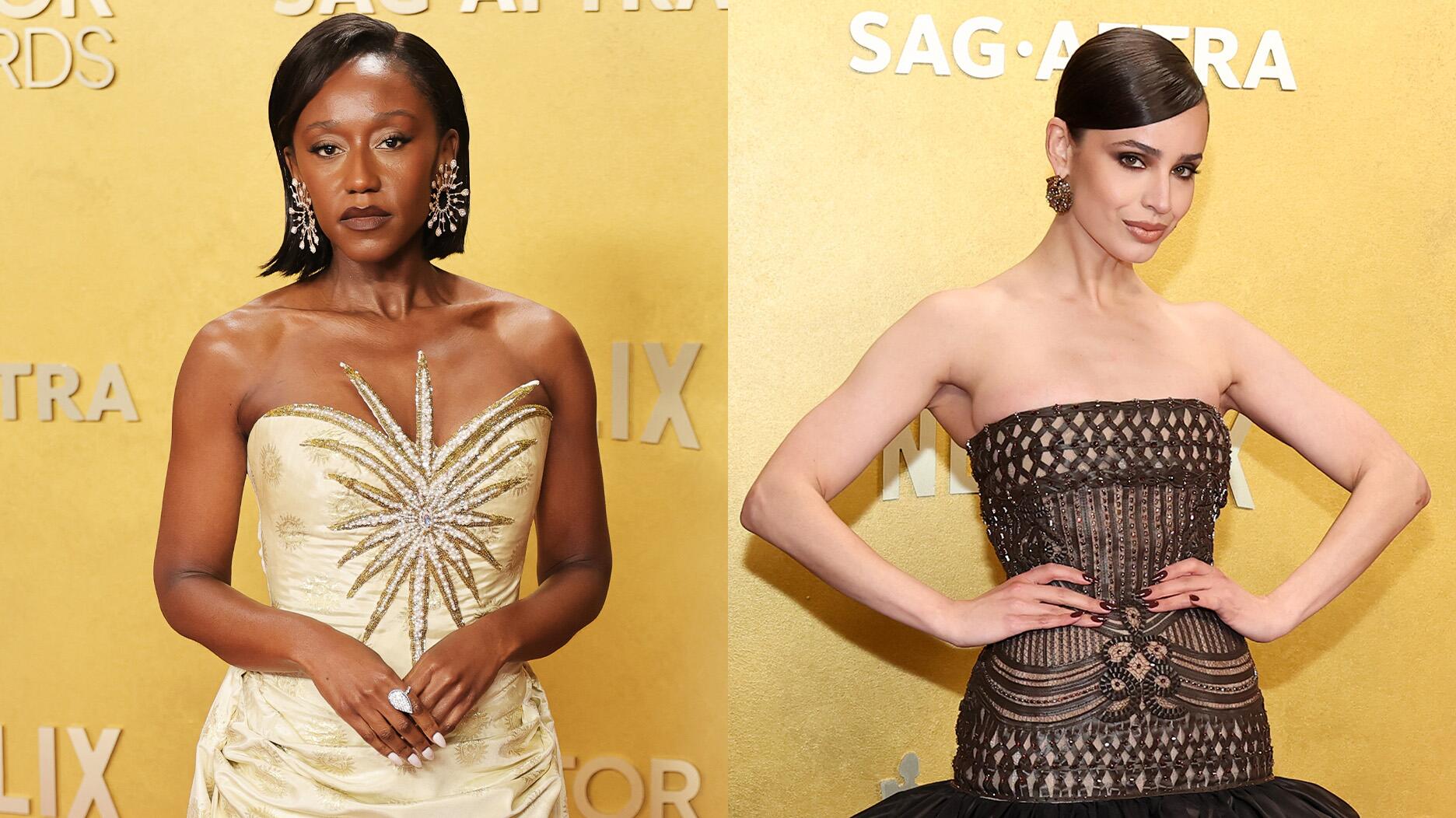Our Pieces of the Week honor the 2026 nominees for the Gem Award for Jewelry Design, Silvia Furmanovich, Cece Fein-Hughes, and Catherine Sarr.
Why there are diamonds in Arkansas
Editor-in-Chief Michelle Graff explores the geologic origins of the diamonds found in The Natural State.
An amateur prospector from Colorado uncovered a beautiful 8.52-carat white rough diamond and the story, as Crater stories usually do, ranked among National Jeweler’s most-read articles for the week.
Whenever we cover discoveries like these at the Crater of Diamonds, two questions always come to mind for me.
Number one, why are there diamonds in Arkansas, and are there diamonds in any other part of the United States? And, number two, are people finding more diamonds in Arkansas recently or are diamond finds just getting more coverage?
To understand why there are diamonds in The Natural State, you have to go back about 300 million years, when the two tectonic plates we now call North and South America collided with each other.
The collision formed the Ouachita (pronounced wash-a-taw) mountain range, which is located just eight miles north of the park.
Now fast-forward about 200 million years, to 100 million years ago, and the site where the park is today blows a gasket, literally (as is common where the Earth’s tectonic plates have converged.)
Instability within the Earth’s mantle forced gas and rock to move toward the surface, and there was a volcanic eruption that blew an 83-acre, funnel-shaped hole into the Earth, Crater Park Interpreter Waymon Cox explained to me via a phone interview recently.
(In case anyone is wondering, he’s called an interpreter because it’s his job to relay, i.e., interpret, information about the park’s geology, history and on how to search for diamonds to visitors.)
Cox said many diamonds, which had been forming underground due to the heat and pressure, came up with eruption.
While many were destroyed in the blast, a fair number also survived, and that’s what visitors find today at the Crater.
So, have the last couple of years, which have their share of good-sized rough finds, been an unusually active time for the park?
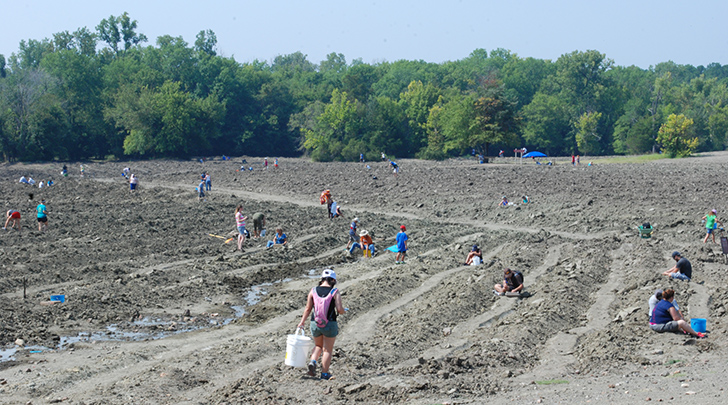

Cox doesn’t answer with an overwhelming yes, saying only that diamond discoveries at the park come and go in waves, influenced by a couple different factors.
First, there is the weather. More rain brings more diamond finds, as it washes away dirt and makes stones easier to find.
Secondly, there are the crowds. One big diamond find seems to begat another, not because people have hit on a particularly rich vein at the site but because big finds get a lot of publicity, bringing more people out to search.
More people searching equals more people turning up diamonds.
The GIA’s Russ Shor, who visited the Crater of Diamonds back in the 1990s when he was a writer for JCK (current JCK Editor-in-Chief Victoria Gomelsky did so as well, much more recently), said diamonds also were found near Rocky Mountain National Park in Colorado in the ‘90s and, going back even farther, JCK reported on diamonds being discovered in Georgia in the 1890s (before National Jeweler even existed).
But, overall, there has never been a huge diamond discovery in the U.S.
Shor notes that kimberlite and lamproite pipes, the two types of pipes that carry diamonds, don’t have an equal distribution of the stones and, of those that do contain diamonds, a smaller percentage still contain an amount of diamonds that make mining worth it.
(Interesting side note: the pipe at the Crater of Diamonds is a lamproite pipe. Shor says the only other known lamproite deposit in the world is the Argyle mine in Australia.)
He also notes that kimberlite pipes often come in clusters, like with the Kimberley Mines in South Africa.
At the Crater of Diamonds, Cox says they did try to mine the site commercially from 1906, when diamonds were first found there, to the 1950s.
In the 1990s, when a man named Bill Clinton was governor, the state decided it was once and for all going to determine if it was a sitting on diamond deposit that was worth mining or not.
As you might have guessed, what the state found was that the site “wasn’t commercially viable,” Cox says.
And so a park it remains. Happy hunting.
The Latest

The 24-piece watch collection is set to debut in spring 2027.

Pooler, who has more than 25 years’ experience in jewelry, is now chief operating officer of Modani Jewels, Soham Diamonds, and SNJ Creations.

Every jeweler faces the same challenge: helping customers protect what they love. Here’s the solution designed for today’s jewelry business.

The reopening of the Waldorf Astoria means a homecoming for the industry group’s annual event, which will take place Saturday.


McCormack looked to the 19th century’s “golden age” of astronomy when designing her new celestial-themed collection.

Nelson will be honored as the inaugural grant winner at the Gem Awards gala on Friday.
With refreshed branding, a new website, updated courses, and a pathway for growth, DCA is dedicated to supporting retail staff development.

The new smart design software allows jewelers to configure, price, and confirm a custom engagement ring in real time for in-store customers.

The 10,000-square-foot diamond manufacturing facility officially opened in late February and employs 50 people.

The MJSA Education Foundation’s scholarships support students pursuing jewelry careers.

The largest white diamond to come to market in the U.K. in more than a decade, the VVS1, I-color stone is expected to top $1 million.

Skelly shares her plans for reimagining the fine jewelry retailer she re-acquired after it faltered last year.

The collection takes inspiration from the emotional space between people, moments, and experiences.

In 2026, the jewelry retailer is celebrating a milestone only a small percentage of family-owned businesses survive to see.

The group of jewelers held a jewelry raffle in support of the Children’s Hospital of Richmond at VCU.

The jewelry giant released preliminary results for the fourth quarter and full year on Monday, with final results slated to come next week.

The retailer also gave an update on its vendor partnerships.

The award-winning actress is the “epitome of modern allure,” the brand said.

The “Bloom” collection draws from the flower power movement of the 1960s and ‘70s with inlay pendants offered in eight colorways.

The unique piece was one of the custom works offered at the foundation's recent silent art auction, which garnered nearly $15,000 in total.

Bulgari named Gyllenhaal as its brand ambassador for his embodiment of artistic depth, intellectual curiosity, and warmth.

Awards were given to four students, one apprentice, and an emerging jeweler.

The top jewelry lot of the late model’s estate sale, hosted by John Moran Auctioneers, was an Oscar Heyman & Brothers for Cartier necklace.
Moses, who started at GIA’s Santa Monica lab in 1976, will leave the Gemological Institute of America in May.

Increased competition, falling lab-grown diamond and moissanite prices, and the rising cost of gold took a toll on the moissanite maker.

The earrings, our Piece of the Week, feature pink tourmalines as planets orbiting around an aquamarine center set in 18-karat rose gold.