Also, a federal judge has ordered that companies that paid tariffs implemented under the IEEPA are entitled to refunds.
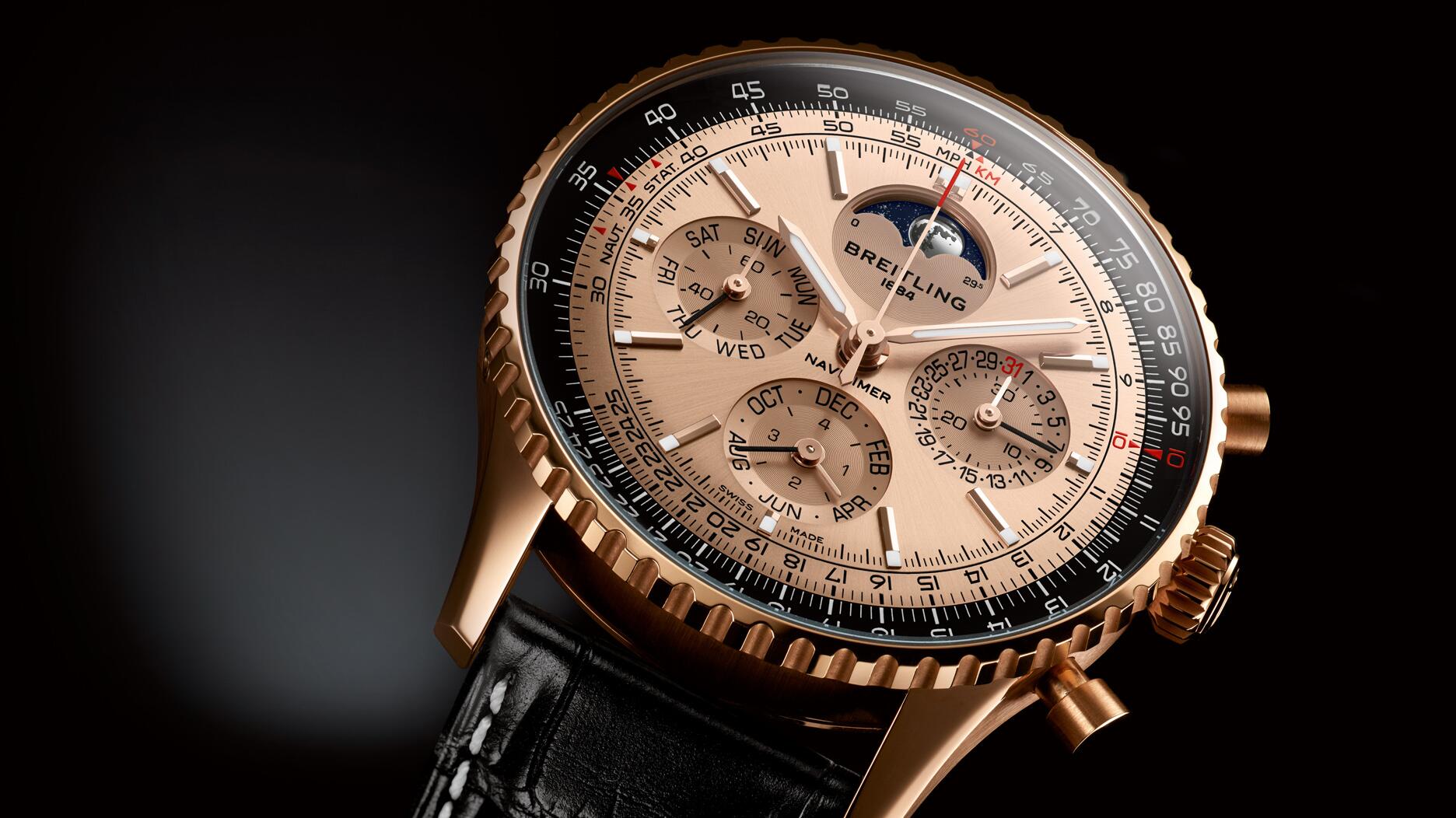
Ask the Watch Guy: Old Style, High-Tech
Jess Gendron gives a history lesson on the mid-19th century high-tech boom that started with a watch company called Waltham.

Most people don’t know it, but there was a high-tech boom in the middle of the 19th century. It began in 1848 when three guys got together in Roxbury, Massachusetts and started a watch company with some radical ideas.
Today, if you have the latest iPhone, you have a piece of modern high-tech. But in the 19th century, high-tech was owning an American timepiece.
Edward Howard, David Davis and Aaron Lufkin Dennison started what would become the Waltham watch factory. The strange ideas these guys had was to make a reliable watch that used standardized parts and was assembled on an assembly line. I know some of you will think that Henry Ford was the inventor of the assembly line but, actually, he invented the automotive assembly line. It was Edward Howard who was the first to use an assembly line for any manufacturing process in 1850, for standardized watches.
What the term standardized parts means is the replacement parts did not have to be made by the watchmaker. Instead, the watchmaker would only need to order parts from the supply house, as all the replacement parts are identical. This was the first such industry to use standardized parts.
Now, getting back to high-tech in the 19th century, the need for accurate time-keeping was getting acute due to the advent of the railroad and the telegraph. American watchmakers heard the call.
Before the 1850s, the only people who could afford a watch or a clock were either very rich private citizen or royalty. Timepieces were then, as today, an outward sign of affluence.
After the Civil War (1861 to 1865), many more American watch companies sprang up, with the need for accurate timekeeping being demanded by railroad companies as well as the public at large. Among the first was Elgin, started in 1866 in Elgin, Illinois. With a loan from “Big Billy” Raymond, mayor of Chicago, the factory was opened on the model that Waltham had created in Massachusetts.
In 1869 the transcontinental railroad was completed, joining the east and west, and with the railroads building new lines of track at a feverish pace, the need for accurate time-keeping was beyond critical--it was necessary. In the 1890s there was a train accident that killed many people. One engineer was using a dollar alarm clock and the other train conductor was using a railroad-grade pocket watch. The engineer with the alarm
After that tragedy Congress wrote the Railway Timekeeping Act, mandating that all railroad employees use railroad pocket watches. Now, what is a railroad-approved watch?
They have all of the following.
-- Lever set: This is the type of watch where you must slide a lever under the crystal bezel to change the time. This was done so the watch could not accidentally have the time changed in someone’s pocket;
-- At least 19 jewels in the movement;
-- A 36-hour run time after winding; most watches of the day only ran approximately 24 hours, though some models were dual time zone and had a 60-hour run time. This was done so the trip from New York City to Chicago could be made on a single wind. Also, having two hour hands one hour apart, it displayed the time in New York City and Chicago;
-- The ability to adjust to five positions, and some even adjusted to six;
-- An open-face case made of nickel or gold-filled; and
-- Accuracy from minus 0 seconds per day and up to plus 5 seconds per day.
During this time, the longstanding Swiss watch companies paid the American watch companies a great honor, if you believe the old proverb that imitation is the sincerest form of flattery.
Swiss watchmakers started using American designs and, what’s even more interesting, they used American names; for example, The Bay State Watch Co. and the Delaware Watch Company. Collectors call these watches “Swiss fakes.”
The reason the Swiss tried to fool people into thinking that their watches were American is because during the entire 19th century, the American watchmakers were the best. People were hot to own a piece of American high-tech. Owning one of these Swiss-made “American” timepieces then is akin to buying an iPhone clone from China today.
America’s entrance into watchmaking made highly accurate timepieces affordable to the working class for the first time in history, which was needed as the country transitioned from a farm-based economy to an urban-factory economy.
The first dollar watches cost $5 and, over time, they became $1 retail. During the 1930s and ‘40s, most American families owned a dollar watch or a low-cost alarm clock made in America.
The American age of watchmaking came to an end with post-World War II tariffs and imports taxes favorable to overseas manufacturers. For example, during the late 1950s and until their demise in 1966, Elgin bought Swiss parts to assemble watches in Puerto Rico because it was cheaper than making the watches in Illinois. It did not take the company far. Elgin went bankrupt in 1966, mostly because the quality had gone downhill. From there, Elgin became a “licensed brand,” meaning someone paid to use the name.
America needs a renaissance in watchmaking. The world is seeking real innovation is a sea of mediocrity, and America is the place to find it. It all began here, so I suggest that we bring it back here.
I, like others in the trade, have nostalgic dreams of the rebirth of American watchmaking. For my part, I have begun making plans to remake the 1890s “Gendron Special.”
At the moment, I’m getting tooled up for the task, only this time it will be a wristwatch and updated with a power reserve and shock jewels. But, that’s a topic for another article.
Jess Gendron is a seventh generation watchmaker, having learned by his father Dan’s side since childhood. He is now the owner of Colorado Timeworks, a watch repair service center in Colorado Springs. He can be reached at talktothewatchguy@gmail.com, and his website is Timeworks.biz.
The Latest

The ever-growing collection, which just expanded with the addition of Olga of Kyiv, features cameos of 12 women from history.

We asked a jewelry historian, designer, bridal director, and wedding expert what’s trending in engagement rings. Here’s what they said.

Every jeweler faces the same challenge: helping customers protect what they love. Here’s the solution designed for today’s jewelry business.

The annual event will be held in Orlando, Florida, from Sept. 14-17.


The “Outlander” star modeled for the digital cover of the magazine’s spring issue, which features a story on her relationship with jewelry.

This year’s annual congress, which will mark the confederation’s 100th anniversary, will take place this fall in Italy.
With refreshed branding, a new website, updated courses, and a pathway for growth, DCA is dedicated to supporting retail staff development.

Beverly Hills was chosen as the location for the brand’s first store, designed as a “private residence for modern monarchs.”

Kering, Apple, and other retailers have reportedly temporarily closed stores in the Middle East region in light of the recent conflicts.

Beth Gerstein discusses the vibe of the new store, what customers want when fine jewelry shopping today, and the details of “Date Night.”

Nearly half of buyers are prioritizing silver and fashion collections this season, organizers said.

The “Live Now. Polish Later.” campaign features equestrians wearing the brand’s jewels while galloping across the icy plains of Kazakhstan.

The precious metals provider has promoted Jennifer Ashworth to the role.

Nelson will be honored as the inaugural grant winner at the Gem Awards gala on March 13.

Experts from India weigh in the politics, policies, and market dynamics for diamantaires to monitor in 2026 and beyond.

The American precious metals refiner’s day-to-day operations remain the same post-acquisition.

These aquamarine jewels channel the calming energy of the March birthstone.

The “Innovative Design” category and award will debut in the Spectrum division of this year’s AGTA Spectrum & Cutting Edge Awards.
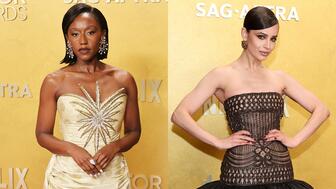
Diamond jewelry was the star of the event formerly known as the SAG Awards.

Consumers were somewhat less worried about the future, though concerns about rising prices and politics remained.

Foerster is this year’s Stanley Schechter Award recipient.

Sponsorships and tickets to the annual fundraising event, set for May 31, are available now.

Chicago police and members of the U.S. Marshals Service tracked down the 35-year-old suspect earlier this week in St. Louis.

Owners of the Ekapa Mine reportedly filed for liquidation about a week after a mudslide trapped five workers who have yet to be found.

A 10-year alliance has also begun to address the shortage of bench jewelers through scholarships, enhanced programs, and updated equipment.

The “Splendente” collection has evolved to feature hardstone letter pendants, including our Piece of the Week, the onyx “R.”