State of the Diamond Industry: Where Does Supply Go From Here?
The 2008 economic crisis, COVID-19, and sanctions on Russian goods have set the stage for an interesting decade for natural diamond supply.

Like coal, oil and gas, diamonds are a non-renewable resource. Molded by a combination of intense heat and pressure over billions of years, they are neither easily formed nor easily replaced.
“For every diamond you take out of the ground, there’s one fewer to be found,” Gemological Institute of America research scientist Evan Smith says.
Still, the industry has not reached a point where the Earth has no more diamonds to give. There are large pockets of land all around the globe that could be diamond targets, Smith says, and exploration is ongoing in remote places like the Melville Peninsula and Baffin Island in the far northern reaches of his home country, Canada.
There are more diamonds believed to be buried deep in another bitterly cold climate, Siberia, and beneath the ocean floor.
South of the Equator, one African nation is poised to become the only country in the world where the three largest diamond miners—Alrosa, De Beers Group and Rio Tinto—all have a presence: Angola.
The question facing the industry is how economically, and in some cases politically, viable is it to get to the ones that are left?
“We aren’t necessarily out of natural diamonds,” industry analyst Paul Zimnisky says. “We’re out of economic deposits at current prices.”
Adding another element of uncertainty is the future of Russian supply, with one of the world’s biggest producers, Alrosa, effectively barred from doing business in one of the world’s biggest diamond markets, the United States.
Heat
Global diamond supply figures maintained by the Kimberley Process (KP), which date back to 2004, show production peaked in the early aughts, climbing to 176.7 million carats in 2005.
It stayed above 160 million carats in 2007 and 2008 before dropping off by more than 25 percent in 2009 (120.2 million carats) in response to the global economic crisis.
Olya Linde, a partner with Bain and Co.’s Energy & Natural Resources practice and one of the authors of the company’s global diamond report for 2020-2021, said prior to the 2008 crisis, the industry had expectations of strong growth.
There was a new middle class coming up in China and India, as well as other Asian countries, that diamond companies were eager and hopeful to capture as their next consumers, bringing growth the industry believed it could not cultivate in the already-mature U.S. market.
These high hopes resulted in “lots of projects in the pipeline,” Linde says, but those projects were put on ice when diamond demand and prices softened during the 2008 crisis.

As the world recovered, the industry benefitted from what Zimnisky describes as a “boom” in diamond buying by Chinese consumers. The surge pushed diamond prices to historic levels in 2011 and rallied investor support for projects that had been paused during the downturn.
In 2016 and 2017, three new large commercial diamond mines came online.
The largest of these was the Gahcho Kué mine in Canada’s Northwest Territories, a joint venture between De Beers Canada and Mountain Province Diamonds. The mine was forecast to produce 4.5 million carats per year but, according to De Beers, surpassed 5 million carats in its first 10 months of operation in 2017.
There was also the Renard mine in Québec, operated by Stornoway Diamonds, and the Liqhobong Diamond Mine in Lesotho, operated by Firestone Diamonds (75 percent interest) and the Lesotho government (25 percent).
These new mines contributed to diamond production reaching 150.9 million carats in 2017—a level not seen since 2008, KP statistics show—and 148.4 million carats in 2018.
Production dropped off to 138.1 million carats the following year, a 7 percent decline but still well above the industry’s range of production from 2011 to 2016.
Toward the end of 2019, however, news began to surface about a cluster of patients in Wuhan, China suffering from an unknown illness that caused their temperature to spike and left them short of breath.
Few people realized it then, but this novel coronavirus would shut down the entire world—some diamond mines included—and dominate the headlines for the next two years.
Pressure
De Beers declined to provide comment for this story, noting it would be inappropriate to discuss specifics about future diamond production.
But in a May 2020 interview with National Jeweler, De Beers CEO Bruce Cleaver did speak a bit about the difficulties involved in closing diamond mines, which he described as “complicated ecosystems.”
In deciding which mines to close and for how long, De Beers had to work out a difficult equation, Cleaver explained—how to keep its workers and the communities that surround its mines safe and healthy while not cutting off their sole source of income by shutting down the operations that support them.
It was a problem diamond miners worldwide grappled with throughout 2020, with production dropping 22 percent year-over-year to a historic low of 107.3 million carats, according to KP statistics.
The biggest decreases came from Russia, Canada, Botswana and Australia, Bain noted in its report.

According to Bain, Alrosa lowered production at Botuobinskaya, Almazy, Anabara and Jubilee, as well as a number of smaller mines. (Alrosa did not provide comment for this story in light of Russia’s Feb. 24 invasion of Ukraine.)
In Botswana—De Beers’ largest source of diamonds by far—production plunged 29 percent for the year, the company’s year-end 2020 figures show.
Canada’s output took a hit from the temporary suspension of operations at two mines there, Renard and Ekati, which reopened under new ownership after former owner Dominion Diamond Mines declared itself insolvent.
In Australia, workers at the Argyle mine in Western Australia hauled out the mine’s last load in November 2020.
The closing of the mine, which had been in operation since 1983, marked the end of an era, both from a practical and a sentimental standpoint.
In its last three years of operation, Argyle produced 14.1 million carats (2018), 13 million carats (2019), and nearly 11 million carats in 2020, Rio Tinto said in its annual report for 2020.
The mine accounted for 10 percent of global production in 2020 and, according to Rio Tinto, was the largest producer of natural colored diamonds in the world.
While most of Argyle’s production consisted of brown diamonds, the mine became famous for the exquisitely colored—albeit relatively small—pink, red and purple diamonds it produced over the years.
Rio Tinto took the best of these stones on a world tour every year as part of the Argyle Pink Diamonds Tender.
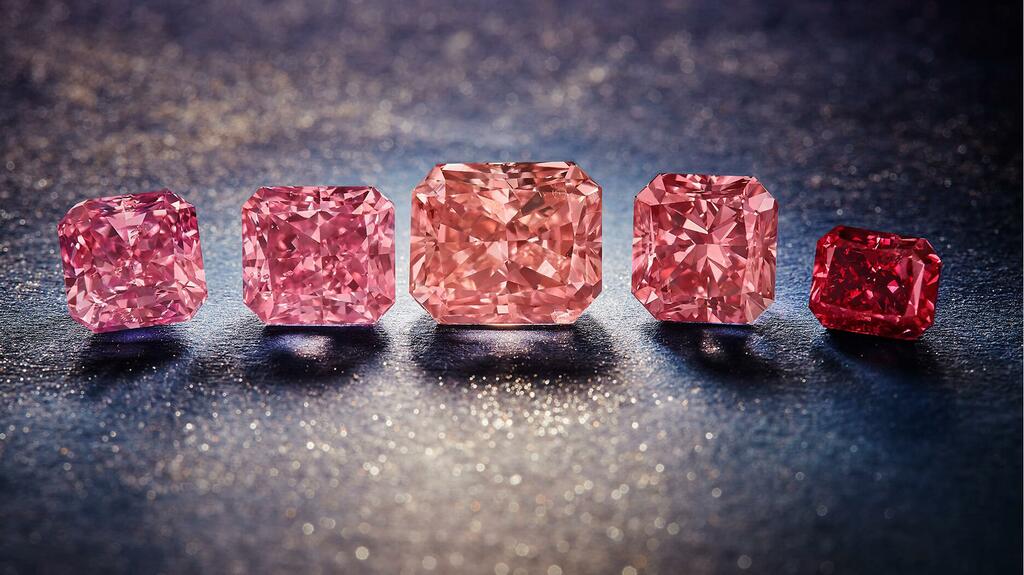

Over the years, the highly saturated stones became coveted collectors’ items, skyrocketing in price and morphing into a luxury brand all their own. (Literally; Rio Tinto retained “Argyle Pink Diamonds” as a brand in its portfolio.)
One diamond dealer with an affinity for the Argyle pinks and purples likened the closure of the mine to “the death of a great artist,” while others note the lasting effect its closure will have on global supply.
As Bain’s Linde notes, 11 million carats a year “is not easy to replace,” but that does not mean companies are not willing to try, particularly as rough diamond prices climb.
Time
Following COVID shutdowns in 2020, diamond jewelry demand rebounded more quickly than expected, spurred by the lack of opportunity to spend money on experiences and travel, and the emotional draw of the stones.
Linde says all the investments the industry has made in recent years in emphasizing storytelling and emotion when selling diamonds paid off when the pandemic hit.
“Diamonds struck a chord. They [diamond marketers] were always telling people about emotional connections and during the pandemic consumers turned to that.”
An unexpectedly bullish 2020 rolled into a 2021 that was equally, and again surprisingly, strong for diamond sales.
Zimnisky says 2021 broke a record for end-consumer demand for diamond jewelry worldwide and there wasn’t enough supply to meet that surge in demand. “But,” he notes, “I don’t think that surge is sustainable.”
He projects annual global diamond supply will mainly stay between 120 million and 130 million carats through the end of the decade. It will peak just above 130 million carats with the ramp-up of Luaxe in Angola, a project of the country’s state-run diamond company, Endiama, and Russian diamond miner Alrosa.
(In an update provided for the digital version of this story, Zimnisky said he now expects diamond supply to come in at the lower end of the 120-130 million carat range, with 130 million carats in 2025 as a ceiling.)
There is diamond exploration underway, including the aforementioned searches on Canada’s Melville Peninsula and Baffin Island, where De Beers has the Chidliak Project it acquired as part of its 2018 purchase of diamond development and exploration company Peregrine Diamonds Ltd.
Zimnisky says he expects Chidliak to be the next mine De Beers activates, and De Beers included it on a list of “notable” diamond projects on the horizon in a recent Diamond Insight Report, though it has not specified a launch date.
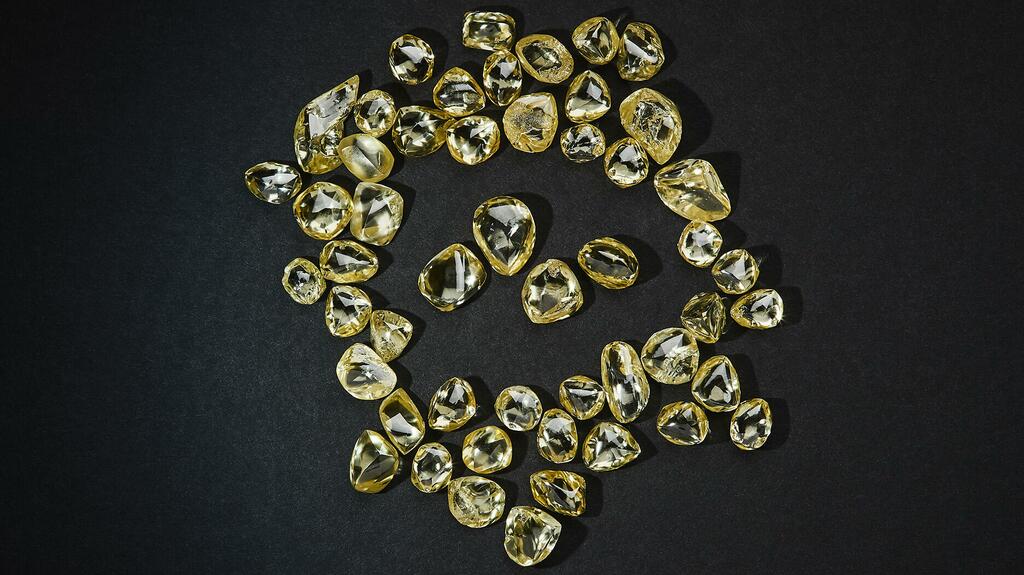

In Australia, efforts are underway to find another source of natural colored diamonds to replace Argyle, and one of the most notable of these exploration efforts involves an old mine.
Australian company India Bore Diamond Holdings and Burgundy Diamond Mines are both vying to restart Ellendale, the mine that once produced high-quality fancy yellow diamonds sold by high-end retailers like Tiffany & Co.
Overall, however, spending on diamond exploration has been declining for years. Data from S&P Global shows companies spent $202 million in exploration in 2021, a fraction of the $986 million spent at its peak in 2008.
It could pick up again if diamond prices stay at their current levels—rough prices rose 21 percent in 2021, according to Bain—or go even higher, but new mines don’t come online overnight, and the industry isn’t likely to see a significant shift in supply this decade.
Zimnisky, however, doesn’t think this is necessarily a negative.
While some might describe the market as undersupplied in the near future, he views 120 million-130 million carats as a “healthy” level of supply for an industry that has, at times, been oversupplied.
He says middle-class Chinese consumers will be the main drivers of diamond jewelry demand going forward, particularly those from the country’s “smaller” cities, outside of behemoths like Beijing and Shanghai, that are growing rapidly.
Indian consumers will be a secondary growth driver.
Bain & Co.’s Linde says the pandemic did not hinder demand for natural diamonds, which has been “very robust” and shows the resiliency of the industry. She says it is unclear if demand will continue to grow at the same pace or undergo a post-pandemic correction.
One thing that is certain, however, is that the market is on the brink of another generational shift.
As the 2020s give way to the next decade, members of Generation Z (currently about 10 to 25 years old) will come into their own as luxury consumers. Retailers will have to figure out what are the right messages and modes of engagement for this new crop of consumers, Linde says.
“It’s a fascinating time, isn’t it?”
The Latest

The April event will feature a new VIP shopping day requiring a special ticket.

Bulgari chose the British-Albanian singer-songwriter for her powerful and enduring voice in contemporary culture, the jeweler said.

In a 6-3 ruling, the court said the president exceeded his authority when imposing sweeping tariffs under IEEPA.
With refreshed branding, a new website, updated courses, and a pathway for growth, DCA is dedicated to supporting retail staff development.

Smith encourages salespeople to ask customers questions that elicit the release of oxytocin, the brain’s “feel-good” chemical.


JVC also announced the election of five new board members.

The brooch, our Piece of the Week, shows the chromatic spectrum through a holographic coating on rock crystal.

Launched in 2023, the program will help the passing of knowledge between generations and alleviate the shortage of bench jewelers.

Raised in an orphanage, Bailey was 18 when she met her husband, Clyde. They opened their North Carolina jewelry store in 1948.

Material Good is celebrating its 10th anniversary as it opens its new store in the Back Bay neighborhood of Boston.

The show will be held March 26-30 at the Miami Beach Convention Center.

The estate of the model, philanthropist, and ex-wife of Johnny Carson has signed statement jewels up for sale at John Moran Auctioneers.

Are arm bands poised to make a comeback? Has red-carpet jewelry become boring? Find out on the second episode of the “My Next Question” podcast.

It will lead distribution in North America for Graziella Braccialini's new gold pieces, which it said are 50 percent lighter.

The organization is seeking a new executive director to lead it into its next phase of strategic growth and industry influence.

The nonprofit will present a live, two-hour introductory course on building confidence when selling colored gemstones.

Western wear continues to trend in the Year of the Fire Horse and along with it, horse and horseshoe motifs in jewelry.

Rossman, who advised GIA for more than 50 years, is remembered for his passion and dedication to the field of gemology.

Guthrie, the mother of “Today” show host Savannah Guthrie, was abducted just as the Tucson gem shows were starting.

Butterfield Jewelers in Albuquerque, New Mexico, is preparing to close as members of the Butterfield family head into retirement.

Paul Morelli’s “Rosebud” necklace, our Piece of the Week, uses 18-karat rose, green, and white gold to turn the symbol of love into jewelry.

The nonprofit has welcomed four new grantees for 2026.

Parent company Saks Global is also closing nearly all Saks Off 5th locations, a Neiman Marcus store, and 14 personal styling suites.

It is believed the 24-karat heart-shaped enameled pendant was made for an event marking the betrothal of Princess Mary in 1518.

The AGTA Spectrum and Cutting Edge “Buyer’s Choice” award winners were announced at the Spectrum Awards Gala last week.

The “Kering Generation Award x Jewelry” returns for its second year with “Second Chance, First Choice” as its theme.

Sourced by For Future Reference Vintage, the yellow gold ring has a round center stone surrounded by step-cut sapphires.