The jewelry giant released preliminary results for the fourth quarter and full year on Monday, with final results slated to come next week.
5 Things to Know About … Burmese Rubies
Senior Editor Brecken Branstrator details a few interesting facts about the stones, which have been allowed back into the U.S. for the first time in nearly a decade.

For my first “5 Things to Know About…” blog post, I chose these stones because they are topical, with the lift of the remaining sanctions and the likelihood that they will be at the upcoming gems shows in Tucson for the first time in a while.
I, for one, hope I can get my hands on at least a few while I’m out in the desert.
In the meantime, here’s are five facts about the gemstones pulled together with the help of a number of experts.
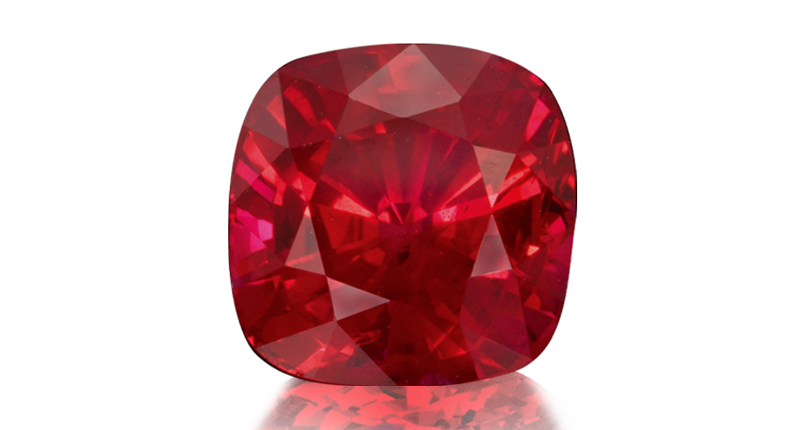
1. The color of fine Burmese rubies comes a result of two factors. According to “Ruby & Sapphire: A Gemologist’s Guide” by Richard Hughes, the first factor is a combination of the slightly bluish-red body color of the gemstone and the “purer” red fluorescent emission, which work together to give the gemstone its high-intensity color.
The second is the presence of “silk”--tiny inclusions scatter light onto “facets that would otherwise be extinct,” giving the color a softness and greater dispersion across the gem’s face.
And while rubies from other sources also can possess the strong red fluorescence and “silk” comparable to those sourced in Myanmar (formerly known as Burma), it’s the particular combination of “fine color … and facetable material (i.e., internally clean)” that puts Burmese rubies at the top.
2. Burmese rubies are much younger than those from East Africa. This is actually true for all rubies created by the collision of the Indian subcontinent with the Asian continent.
During certain times in history, tectonic movement has resulted in large-scale shifts in the Earth’s surface, resulting in mineral formation and creating regions called orogenic belts. A lot of the finest ruby and sapphire mines fall into such zones, according to Hughes’ book.
The Pan-African orogeny happened about 750 to 450 million years ago, the result of which created gem deposits in Kenya, Tanzania, Mozambique, Madagascar, Sri Lanka and southern India.

Meanwhile, the activity that resulted in the Himalayan region--the Indian subcontinent colliding with the Asian continent--occurred “just” 45 to 5 million years ago. This created ruby and sapphire deposits from Afghanistan and Tajikistan through Pakistan, northern India, Nepal and Myanmar, and onward to China and Vietnam.
Though there currently is no easy way to age-date rubies, Hughes said if we could, it would provide a method for separating Himalayan rubies from those sourced in East Africa and Sri Lanka.
3. There isn’t a great deal of fine quality rubies coming out of Burma right now. Most of the alluvial deposits in the Mogok region are mined out, according to Hughes.
He said the best gemstones come from alluvial deposits because millions of years of weathering naturally removes the impure cracked portions, which leaves behind the purest part of the crystal.
But now, without the alluvial sources, mining increasingly involves hard rock, which has lower yields and keeps production low.
In a blog post published shortly after the ban was officially lifted in October, Omi Gems also noted that even while the ban was in place in the U.S., Burmese rubies still were being exported to other countries but “supply was still not meeting that (high) demand.” This means that there’s no great supply ready to be sent to the U.S., Omi added, and that prices are likely to remain high.
4. Burmese rubies can be compared to fine rubies from Mozambique. While there are a lot of great rubies coming from other sources, it was the discovery of the fine stones from Mozambique in the late 2000s that made a great splash in the gem world, especially given the ban on Burmese material.
Where a strong presence of iron gives many other sources a slightly brownish hue, the material from Mozambique varies in iron content, so its rubies can have a fluorescence and color hues in similar to the classic colors of Burmese rubies, according to gemologist Richard Wise’s “Secrets of the Gem Trade (Second Edition).”
In his book, Wise wrote that he has seen several stones from Mozambique that “rival, in hue, saturation the best Burma has to offer.”
This is good news for the industry given that there’s so little coming out of Myanmar right now, as mentioned before, and as Mozambique rubies today make up a large part of what’s on the market.
Wise, in fact, estimates that about 85 percent of the ruby market today is made up of Mozambican goods.
And as production from Myanmar continues to decrease--assuming the supply of Mozambican rubies remains strong--he price gap between Burmese and African rubies likely will continue to get smaller.

5. The conflict surrounding Burmese rubies has changed. The U.S. declared a “national emergency” with respect to the Burmese military’s rise to power in 1997 and started to impose sanctions on the country a short time later.
The U.S. government then specifically targeted the import of gemstones with the Tom Lantos Block Burmese JADE (Junta’s Anti-Democratic Efforts) Act of 2008, noting the human rights violations of the ruling regime and how it was evading sanctions by concealing gemstone origins to continue their export to the U.S.
Now, as we all know, the remainder of those sanctions have been lifted and rubies can once again be shipped into the country.
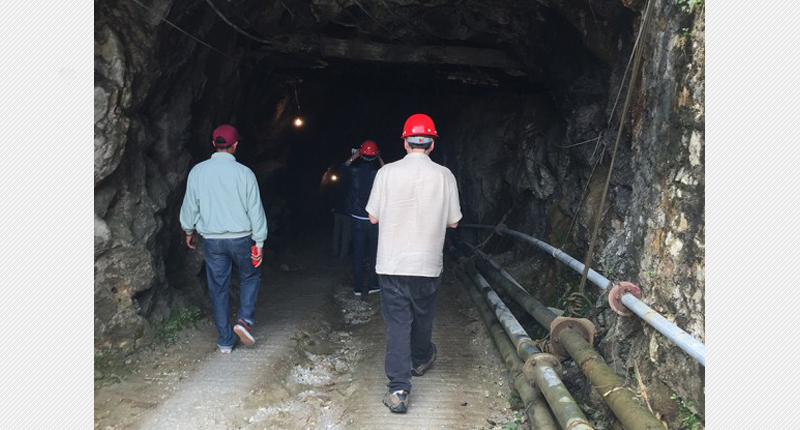
In October, leaders from the American Gem Trade Association and Jewelers of America took a trip to Myanmar to discuss trade between countries. While they were there, the group traveled to Mogok, the center of the gemstone trade in Myanmar and traditionally the source for the best rubies, to visit mines and with miners and dealers.
The AGTA has since released a report on its findings and the recommendations the delegation is making to officials of Myanmar.
The report states that “most of Myanmar’s rubies are in conflict-free zones, with the exception of small deposits in Mongshu in Shan State.”
Thus, the safety of workers, mine operators and prospectors, is greater and the “likelihood of indirectly funding armed conflict is less,” the report states.
(This is, of course, looking specifically at rubies in Myanmar. Jade and the problems surrounding it are a separate issue.)
Still, the AGTA hade made recommendations to the country’s officials on how to make their gemstone industry more transparent and develop it--including separating jade from other gemstones when it comes to licenses and regulations--and will continue to help it develop in the future.
The Latest

The retailer also gave an update on its vendor partnerships.

The award-winning actress is the “epitome of modern allure,” the brand said.

Every jeweler faces the same challenge: helping customers protect what they love. Here’s the solution designed for today’s jewelry business.

The “Bloom” collection draws from the flower power movement of the 1960s and ‘70s with inlay pendants offered in eight colorways.


The unique piece was one of the custom works offered at the foundation's recent silent art auction, which garnered nearly $15,000 in total.

Bulgari named Gyllenhaal as its brand ambassador for his embodiment of artistic depth, intellectual curiosity, and warmth.
With refreshed branding, a new website, updated courses, and a pathway for growth, DCA is dedicated to supporting retail staff development.

Awards were given to four students, one apprentice, and an emerging jeweler.

The top jewelry lot of the late model’s estate sale, hosted by John Moran Auctioneers, was an Oscar Heyman & Brothers for Cartier necklace.
Moses, who started at GIA’s Santa Monica lab in 1976, will leave the Gemological Institute of America in May.

Increased competition, falling lab-grown diamond and moissanite prices, and the rising cost of gold took a toll on the moissanite maker.

The earrings, our Piece of the Week, feature pink tourmalines as planets orbiting around an aquamarine center set in 18-karat rose gold.

“The Price of Freedom” campaign video for International Women’s Day confronts the quiet violence of financial control.

Also, a federal judge has ordered that companies that paid tariffs implemented under the IEEPA are entitled to refunds.

The ever-growing collection, which just expanded with the addition of Olga of Kyiv, features cameos of 12 women from history.

We asked a jewelry historian, designer, bridal director, and wedding expert what’s trending in engagement rings. Here’s what they said.

The annual event will be held in Orlando, Florida, from Sept. 14-17.

The “Outlander” star modeled for the digital cover of the magazine’s spring issue, which features a story on her relationship with jewelry.

This year’s annual congress, which will mark the confederation’s 100th anniversary, will take place this fall in Italy.

Beverly Hills was chosen as the location for the brand’s first store, designed as a “private residence for modern monarchs.”

Kering, Apple, and other retailers have reportedly temporarily closed stores in the Middle East region in light of the recent conflicts.

Nearly half of buyers are prioritizing silver and fashion collections this season, organizers said.

The “Live Now. Polish Later.” campaign features equestrians wearing the brand’s jewels while galloping across the icy plains of Kazakhstan.

The precious metals provider has promoted Jennifer Ashworth to the role.

Nelson will be honored as the inaugural grant winner at the Gem Awards gala on March 13.

Experts from India weigh in the politics, policies, and market dynamics for diamantaires to monitor in 2026 and beyond.