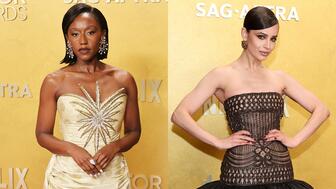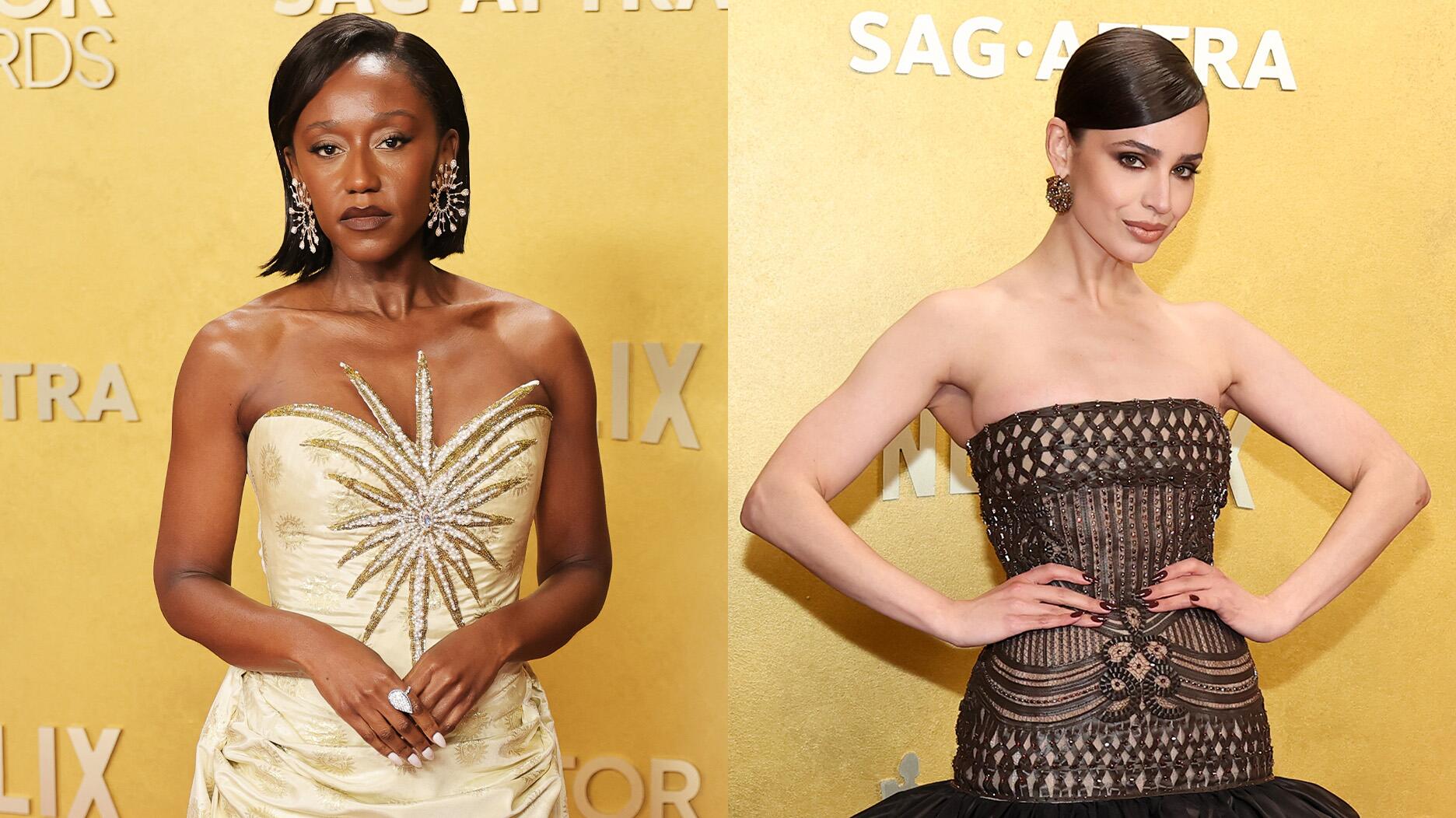Our Pieces of the Week honor the 2026 nominees for the Gem Award for Jewelry Design, Silvia Furmanovich, Cece Fein-Hughes, and Catherine Sarr.
5 Things to Know About … Ammolite
Senior Editor Brecken Branstrator details 5 interesting facts about the gemstone that is cut from the fossilized shells of a prehistoric creature.

There’s a gemstone that’s garnering more attention that could speak to those who not only like gemstones with provenance but also with a pretty cool back story.
Ammolite, the iridescent gemstone that’s actually cut from the fossilized shells of a prehistoric creature, comes from only one source only.
The gems have a truly fascinating story; here are five things you should know about them.
1. Nomenclature is key. There’s a difference in the names when it comes to gem versus fossil.
According to the GIA’s Gems & Gemology, ammonites were squid-like creatures with sharp, beak-like jaws, a spiral shell and tentacles. They went extinct about 66 million years ago.
Ammolite, meanwhile, is the trade name for the iridescent, nacreous layer of the shell of fossilized ammonite. Commercial quantities of gem-quality ammolite are only known to come very a few specific types of ammonite shells, the G&G article said.
The GIA said that a number of things must happen for ammonite to become an ammolite gem. It has to be buried quickly, deprived of oxygen, protected from heat and excessive weight, and not be scavenged.

2. They only come from one place. The ammonite sea creatures were around long before there were seven continents. According to the GIA, there were only two large landmasses--Gondwana and Laurasia--on the Earth’s surface when they lived.
This helps explain how the water mass in which they lived (the Bearpaw Sea) during the Late Cretaceous period now is a rock formation that stretches through Montana, and Alberta and Saskatchewan, Canada.
While fossilized ammonites can be found in several places around the world, a small area within the Bearpaw Formation, the name for the area leftover from where sediment settled on the bottom of sea, in Southern Alberta, Canada, is the only location where they have been turned into gemstones.
The International Gem Society estimates that only about 5 percent of the ammonites found in Alberta have suitable gem material on the shell surface.
3. They are fairly new to the gem and jewelry world. Despite their historic formation, ammolite is one of the few new natural gems to be introduced into the market in the past 70 years.
It only started to appear in jewelry in the 1960s and was recognized as an organic gemstone in 1981 by the
And like tanzanite and sugilite--introduced to the trade in 1967 and 1980, respectively--ammolite occurs in large enough quantities to make it “economically significant,” Gems & Gemology said.

4. They vary in color and some colors are more valuable. Ammolite can come in any color in the rainbow but most are green and red. Blue and violet are rare and, typically, more valuable.
As is true for most gems, cost depends greatly on the color, which is graded on a scale from one to five. The brightness of the gem also is judged.
Ammolite also can show patterns of fractures on the surface, like stained glass. The GIA said that while fracture ammolite was common in the past, production today mostly includes sheet ammolite.
5. Demand is expected to increase. Korite International in Canada, the largest supplier of ammolite, said that it will quadruple the size of production within the next 12 months as more consumers across the world start to discover and buy the gemstone.
According to a local news story, the company currently is mining two acres a year but will expand to eight over the next year. Production is expected to increase from the current eight million carats per year, which already was increase over last year, to double within the next two years to meet demand across the globe.
The company even has targeted the United States as one of the markets where it believes ammolite could do well.
The Latest

The 24-piece watch collection is set to debut in spring 2027.

Pooler, who has more than 25 years’ experience in jewelry, is now chief operating officer of Modani Jewels, Soham Diamonds, and SNJ Creations.

Every jeweler faces the same challenge: helping customers protect what they love. Here’s the solution designed for today’s jewelry business.

The reopening of the Waldorf Astoria means a homecoming for the industry group’s annual event, which will take place Saturday.


McCormack looked to the 19th century’s “golden age” of astronomy when designing her new celestial-themed collection.

Nelson will be honored as the inaugural grant winner at the Gem Awards gala on Friday.
With refreshed branding, a new website, updated courses, and a pathway for growth, DCA is dedicated to supporting retail staff development.

The new smart design software allows jewelers to configure, price, and confirm a custom engagement ring in real time for in-store customers.

The 10,000-square-foot diamond manufacturing facility officially opened in late February and employs 50 people.

The MJSA Education Foundation’s scholarships support students pursuing jewelry careers.

The largest white diamond to come to market in the U.K. in more than a decade, the VVS1, I-color stone is expected to top $1 million.

Skelly shares her plans for reimagining the fine jewelry retailer she re-acquired after it faltered last year.

The collection takes inspiration from the emotional space between people, moments, and experiences.

In 2026, the jewelry retailer is celebrating a milestone only a small percentage of family-owned businesses survive to see.

The group of jewelers held a jewelry raffle in support of the Children’s Hospital of Richmond at VCU.

The jewelry giant released preliminary results for the fourth quarter and full year on Monday, with final results slated to come next week.

The retailer also gave an update on its vendor partnerships.

The award-winning actress is the “epitome of modern allure,” the brand said.

The “Bloom” collection draws from the flower power movement of the 1960s and ‘70s with inlay pendants offered in eight colorways.

The unique piece was one of the custom works offered at the foundation's recent silent art auction, which garnered nearly $15,000 in total.

Bulgari named Gyllenhaal as its brand ambassador for his embodiment of artistic depth, intellectual curiosity, and warmth.

Awards were given to four students, one apprentice, and an emerging jeweler.

The top jewelry lot of the late model’s estate sale, hosted by John Moran Auctioneers, was an Oscar Heyman & Brothers for Cartier necklace.
Moses, who started at GIA’s Santa Monica lab in 1976, will leave the Gemological Institute of America in May.

Increased competition, falling lab-grown diamond and moissanite prices, and the rising cost of gold took a toll on the moissanite maker.

The earrings, our Piece of the Week, feature pink tourmalines as planets orbiting around an aquamarine center set in 18-karat rose gold.